Adaptation to climate-change involves changes to the natural and social environment in order to decrease the likelihood of adverse climate effects. Adaptation can occur at various levels, including the national, local and international. It includes physical, structural, and institutional approaches, and includes early warning systems for natural disasters. It can also include taking advantage of potential climate-related benefits.
The climate change impacts are felt on many levels including weather, sea level and water resources. These changes are expected increase the frequency of extreme weather events. These changes can also impact the availability of water throughout the year. This can result in more frequent droughts and floods. Some regions will see longer growing seasons as a result of the warming. Rapider climate change can make adaptation more difficult at higher levels.

A variety of adaptation solutions can be implemented, from building flood defences to redesigning business operations. Adaptation actions have the potential to strengthen livelihoods, increase innovation, and help nature recover. For example, a California town uses goats to clear vegetation from the streets, and a project in Papua New Guinea has put people in a better position to deal with storms.
Adaptation is an iterative process. This means that adaptation will improve as more information is available about the impacts of climate change. Successful adaptation requires sustained engagement by all stakeholders. It should also consider vulnerable people.
Several ecosystems and species are now near hard adaptation limits, meaning that they are unable to adapt to the current state of the environment. These limits can be caused by cultural, financial and social barriers. Many countries have taken steps to implement and develop climate adaptation strategies.
Countries with higher development and adaptive capacity are believed to be able to respond effectively to the changing climate. However, low-income societies may not be able to adapt quickly enough. As a result, individuals with strong social institutions can be regarded as having greater adaptive ability. However, these characteristics are not necessarily associated with higher equity or well being.

Adaptation is crucial because it allows communities to prepare for and respond to future changes. For example, the coast may require new sea walls or restoration of wetlands. Cities are also implementing community energy plans and installing more draining pavements.
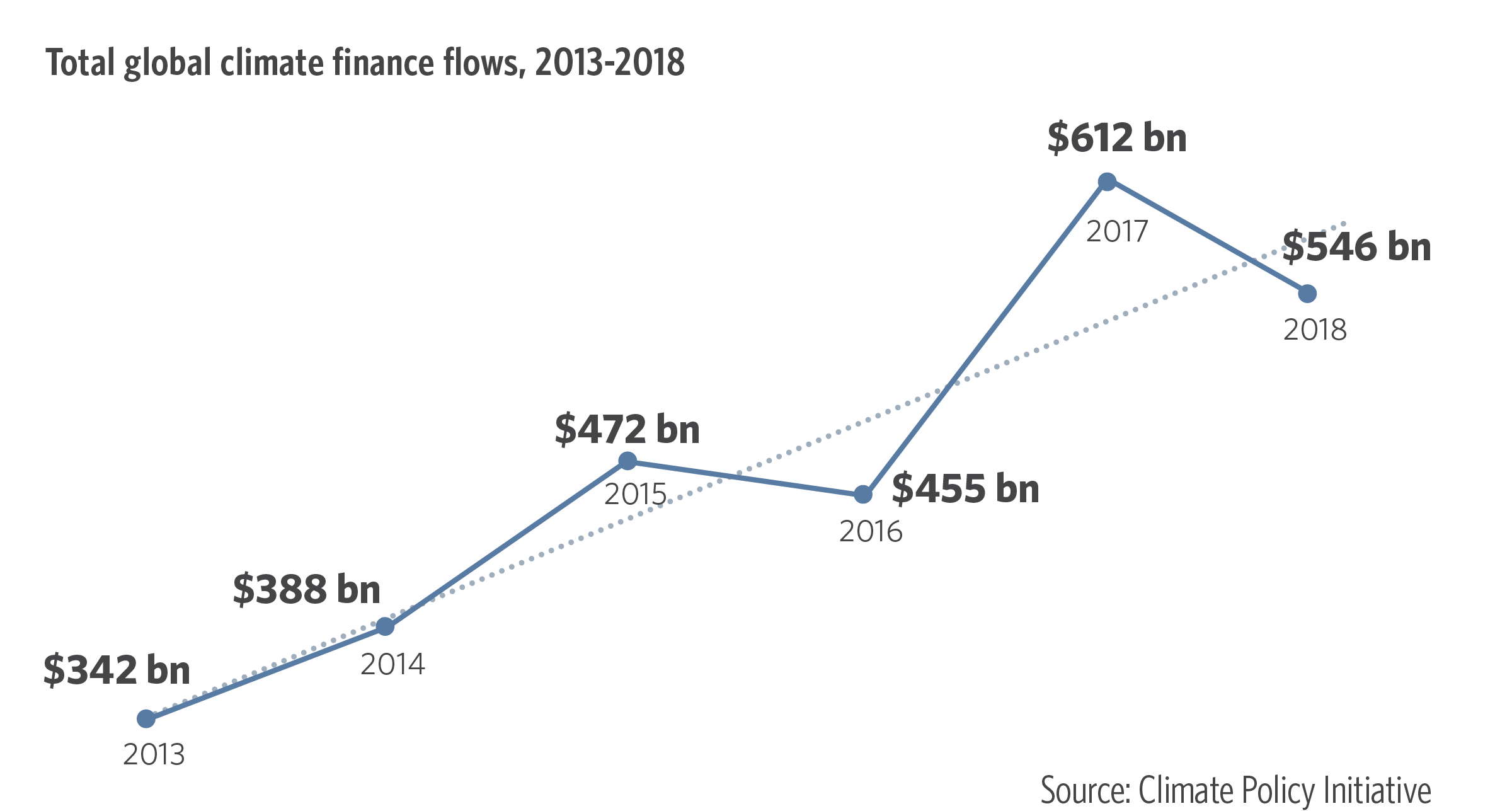
Despite this progress, many countries remain unable to adequately address climate change. A lack of resources is especially evident in low-income countries. They are unable to invest in storm-resistant infrastructure or build sea walls. There is also a shortage of funding for adaptation measures in aquaculture, fisheries, and forestry.
Adaptation, which is crucial in reducing the climate change impact, is key. It can yield multiple benefits, such a reduction in food insecurity and an increase in the productivity of fishing stock stocks. Climate adaptation investment can reduce the cost of future investments.
FAQ
How does climate change affect the world's oceans and marine life?
What are the impacts of climate changes on the oceans, and marine life worldwide?
Since its inception the climate change has had an impact on the world's oceans, and the marine life within them. Constant oceanic warming due to the depleted ozone layer causes drastic disruptions in marine ecosystems resulting in a decrease in species and coral bleaching.
Climate change is also responsible for unpredictable weather patterns and stronger storms, which can lead to dangerously high sea levels. Changes in temperature can lead to a decrease in oxygen levels, which could cause "dead zone" conditions in which marine life is scarce.
Ocean acidification is also a result of excess carbon dioxide that has built up in the oceans. This is due to climate change. Ocean acidification can raise pH levels, making it difficult for animals to adapt like crabs, clams or oysters.
Higher temperatures can alter the natural habitats of certain species by changing their locations or shrinking them, making them uninhabitable. An increase in ocean pressure can cause a drastic imbalance between predators & prey and lead to the extinction of many species.
The impacts of climate change have rippled through entire ecosystems. They impact multiple species either directly or indirectly through evaporation, decreasing water volumes, or sharp temperature changes. This could jeopardize any sustainable development for fishing and other maritime activities. Global climate change continues to decimate entire species, changing future lives on earth and below the surface of the oceans.
How does the politics of climate change impact global efforts to address it?
Climate change is a highly politicized issue that has created a great deal of division among nations, governments, and individuals. Politicians of many actors influence the implementation of actions to address climate change. It is becoming difficult to reach consensus on global efforts for addressing this urgent environmental crisis.
Most scientists agree that humans are causing climate change. This is why it is urgent to act. These issues are often subject to political interference that can hamper global cooperation in order to implement sustainable energy practices, preserve natural habitats, find viable technological solutions and other interventions related to climate change.
Many governments around the globe want to protect business interests and enforce policies that restrict business activities. This often clashes with regulations that experts recommend for effectively addressing climate change. Without strong international commitments and wide-spread international action, it can be very difficult for any individual state or group of nations to address climate change effectively through legislation.
Different power dynamics can make it difficult to achieve full consensus on the best ways to address climate change. Countries with more economic power often appoint their own representatives to represent them on international bodies responsible for negotiations over the environment - this can lead to lopsided discussions of those countries' perceived interests versus the collective interest of all involved parties. At both the national and international level, there have been extensive discussions about potential side effects of radical changes like geoengineering.
Also at the grassroots level, grassroots movements have fought against powerful opponents such as corporate ownerships. These lobbies are trying to preserve politically favorable positions for their industry especially when it is about funding research into alternative sources of energy production or enforcing Renewable Energy Technology mandates. If individual governments want to make valid progress in the subject matter themselves instead of seeking short-term benefits or spectacles, they must be clearheaded about possible outcomes.
If we are to achieve a coordinated effort to address our current environmental crisis, it is crucial to properly distribute resources and be aware of political divisions among nations.
How can we address climate change by addressing the role of the energy industry?
The role of the energy sector in climate change is immense. Global warming is caused by the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This traps heat and causes an increase in Earth's average temperature.
To address this issue, energy sources must transition away from carbon-emitting fuels like coal and natural gaz and instead turn to renewable energy sources like solar, geothermal, wind, and other renewable sources. This change can be made by government policy, incentives, and investments in innovative technology, such as hydrogen fuel cells. Businesses and households can reduce their carbon emissions by investing in infrastructure to support the use of renewable energy sources.
Other options include switching away from petroleum-fueled cars, moving towards electric vehicles, and public transport. Governments have the power to encourage and support investment in cleaner modes for transportation.
Additionally, companies must implement green business practices within their operations to reduce overall carbon footprints by implementing better insulation systems for offices or implementing energy efficiency plans for production facilities. This can help drastically reduce operational costs while simultaneously improving environmental performance metrics.
These initiatives must be championed not just at the company level but also at the government level for them to be truly effective; increasing taxes on pollution products encourages individuals to switch away from harmful practices without forcing them financially outcompeting polluters by providing vouchers or subsidies for low-carbon products will create an ongoing market to support sustainability efforts moving forward. This is why tackling climate changes requires both private industry as well as private citizens to make a difference. By switching to green energy and adopting environmentally friendly practices, we can help to ensure that the future generations of people are affected positively.
What is the role of individual and community members in addressing climate changes?
Climate change is one our greatest contemporary challenges. This is a problem that affects everyone. We must all pay attention to it and take action individually to make a difference.
Individuals play a vital role in addressing climate change and reducing its impacts. Your everyday behaviors could include reducing waste, conscious eating, changing your lifestyle, such as becoming vegetarian, choosing sustainable clothing and decor, and using public transport more frequently. They can also participate in political advocacy and help promote sustainable initiatives in their local communities.
It is important that communities are involved in the larger climate change effort. They can help reduce carbon emissions by promoting sustainable energy sources, improving infrastructure for electric vehicles and cycling, and encouraging waste management through composting. Collaboration between different communities across cities and countries is fundamental for achieving success in this mission.
This will help individuals become aware of the issues at stake and understand how to contribute positively to tackling them. This will make individuals more aware of the problems and help them understand the interconnectedness with societies farther away than their own.
Employers bear a huge responsibility for combating climate change. It is important that they adopt sustainable corporate practices and use green alternatives wherever possible.
Therefore individuals' actions plus community-wide policies together with business transformation will contribute immensely towards creating solutions against global warming and collectively defending humanity against longer terms harmful effects growing out from climate change.
What are the current international efforts to combat climate change?
The current international climate-change effort is moving forward with unprecedented momentum and unity. Countries all around the globe are increasingly joining forces to find solutions to climate change.
The Paris Agreement is an international framework that encourages collective action. It also provides a framework to allow individual countries and regions to set voluntary targets to reduce emissions. The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change is also providing guidance to policy and piloting innovative initiatives, such as carbon market mechanism.
Progress is also being made in specific regions; for example, The European Green Deal is a comprehensive package of legislation aimed at recreating Europe's economy with sustainability at its core, while countries of the African continent have committed to the African Renewable Energy Initiative which aims to increase Africa's share of global renewable energy production.
Apart from policy changes, action is visible across sectors and industry. Cities are actively transitioning to sustainable public transport systems. Society at large is adopting more sustainable lifestyles. Companies have been innovating technologies to lower emissions. Investors are switching away from fossil fuels to invest in renewables.
The wealthy countries represented under the OECD committee have adopted common standards for reporting national actions on climate change through the Common Reporting Framework (CFR) called the 2021 Guidelines.
These efforts signify a new level of importance for climate action. To meet climate goals, both governments and civil society must continue to build on the momentum.
What are the impacts of climate change on biodiversity, ecosystems and species?
Climate change is having a wide range of effects on biodiversity as well as ecosystems. Today's issues that impact wildlife and ecosystems include rising temperatures, increased sea levels and extreme weather events.
These changes can result in shifts of habitat areas, disrupting food chains or affecting population numbers or distributions. With potentially devastating consequences for biodiversity, ecosystems and their functioning, these shifts in climate conditions could cause significant impacts. Water availability can be affected by changes in hydrological cycles.
Climate change also causes rising temperatures, more frequent extremes like droughts and flooding. This puts additional stress on fragile systems like coral reefs and tropical rainforests. It is estimated that up to 30% of animal species could become extinct due to climate change by 2050, which would spark a cascade of further losses within ecological communities.
Climate change is therefore a considerable threat not only to biodiversity but also to human societies that depend on functioning ecosystems for food, fresh water, timber, and other services. To mitigate its effect efforts must be made at all levels to reduce global warming trends and future damages should be avoided where possible with careful management practices.
How can climate change impact food security and agriculture?
Climate change and global warming are directly impacting agriculture and food security. The changing climate can impact rainfall patterns and temperatures as well as soil moisture levels. Extreme weather is also possible. This can disrupt farming activities, reduce crop yields and lead to losses of agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures may lead to an increase in pests and diseases that can affect crops. They can also result in shifts of ranges suitable to agricultural production. This could lead to an increase in food prices and a higher incidence of hunger worldwide.
Rising sea levels are a threat as they could flood important agricultural land along the coast. This would lead to an increase in salinity in wetlands that support important crops. Changes in climate also have an impact on livestock production. In summer, high temperatures can lower fertility rates in animals like sheep and cattle. This can result in lower milk yields, which can worsen food insecurity.
Global warming and climate changes are interrelated. But, governments around world are working to mitigate the effects of these changes through adaptation strategies. This includes promoting sustainable methods like crop rotation techniques and genetic diversity through conservation of native seed varieties. These help to protect against adverse impacts from extreme weather conditions and other environmental stressors due to the changing climate. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
Farmers around the globe must adopt technology that is more sensitive to climate changes to ensure food security in a changing environment. Existing infrastructure must be improved to allow for the appropriate action when necessary. This includes stabilizing irrigation networks that have adequate access to water during periods when there are less water sources due either to extreme downpours or warmer climates. Collaboration between different stakeholders is needed to ensure that the quality nutrition guidelines are adhered to in all climates.
Statistics
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to educate your community about climate change and mobilize action
Climate change education can be in many forms, from online resources and interactive educational tool to classroom activities, simulations, experiential learning programs, and classroom activities. These are the essential elements of effective climate education:
-
The goal is to provide practical knowledge and skills for the people who are interested in this subject.
-
Demonstrating that people can make a real difference.
-
Participants are invited to engage in an open conversation about possible solutions
-
Inspiring action through shared experiences
Teachers can help communities to reduce their environmental footprints by offering comprehensive lessons in climate change for both adults and students.
A unique way to engage people in meaningful dialog is to link scientific research with real world examples. The best practices and case studies can provide participants with the chance to experience positive outcomes firsthand. This can help them innovate or create replicable measures in their own communities.
Incorporating action-oriented activities into educational curriculums empowers participants with the mental tools they need -- such as creating campaigns, forming petitions, or local actions -- enabling them to become agents of social and political transformation or sustainability improvement initiatives. In addition, individual agency emphasizes the importance of participating in reducing emissions. It also shows participants' collective contributions to a greater outcome. A key element in policy-making is to involve stakeholders as early as possible. This encourages their active involvement at every stage of the process and could result in better outcomes for all. If we work together to improve public understanding and to take the appropriate action to reduce greenhouse gases emissions, then we might be in a position to create an environment that allows us to address urgent issues with our attention being focused where it is most necessary. In this way, we can all help to achieve our collective goals.