The change in the climate of nature is caused by the greenhouse gases. The heat is transferred from Earth via the atmosphere and oceans. They interact with one another. Climate changes can take place over many hours or even decades depending on where they occur. Weather is an important climate indicator, since it can have an effect on seasonal rainfall conditions. The climate is influenced largely by the oceans, ice, carbon cycle, and other factors. However, many of these elements are slow in response.
The deep ocean is slow to respond to climate change. There may be delays in climate change responses due to feedbacks among the ice sheet and deep ocean. These processes have the potential to influence the frequency of extreme events. Recent analysis has shown that these feedbacks could account approximately 20% of mitigation requirements by 2050.

Some solutions to climate change involve restoring ecosystems. These include natural wetlands, forests, and coastal ecosystems. These ecosystems contribute to reducing climate change's impacts by increasing carbon storage. They protect biodiversity, provide clean air, and secure water supplies. They can also encourage synergy between Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Climate change is one the most pressing and difficult science problems of our times. Many scientists are currently trying to determine the causes and consequences of climate change. Understanding the impacts climate change has on both nature and society is essential. It can lead to drastic changes in the adaptive capability of species and the overall climate system's sensitivity.
Despite the urgency, evidence is mixed regarding the effectiveness of nature-based climate solutions. Several factors are needed to ensure their reliability. The benefit of nature-based strategies is not always obvious. Second, they require a thorough understanding of the biome, its ecological resilience, and how it functions. Also, these solutions can be hard to monetize.
A recent analysis however found that nature-based solutions could help to mitigate the impacts of climate change. In particular, natural forests could secure water supplies and reduce flood risk. Another benefit of natural wetlands are the reduced erosion of soil.
Nature-based solutions offer significant advantages over engineered alternatives. However, their performance is still uncertain. They must be combined quickly with a reduction in greenhouse gas emission. They also have to be promoted and funded, and they may require training and outreach.
Recent studies have shown that nature-based mitigation strategies are cost-effective and efficient. They can contribute as much as 20% to the mitigation efforts by 2050 if they are combined with rapid reductions in emissions.
For example, natural wetlands are able to mitigate flooding and landslides. Moreover, natural forests and coastal ecosystems can increase biodiversity. Likewise, some ecosystems are already transitioning to alternative states under climate change. Some species that were once found only in tropical or boreal communities are now finding their way into temperate ones.
FAQ
What is the climate impact of land use and deforestation?
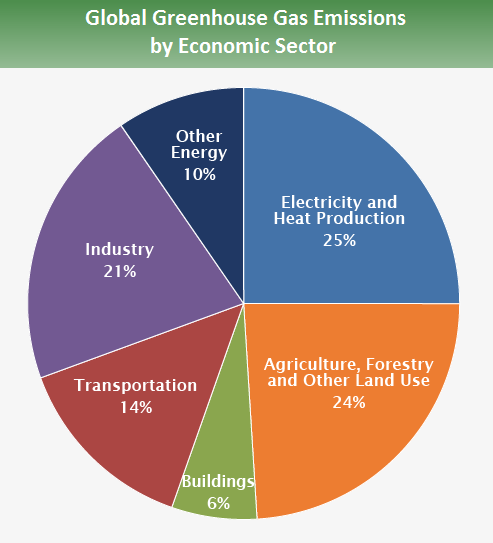
The climate is directly affected when land use and deforestation are both occurring. Carbon dioxide, which is the most important greenhouse gas on Earth, can't be absorbed by trees if they are removed or burned. Carbon dioxide is therefore less removed from the atmosphere when trees are deforested or burned for agricultural purposes.
Changes in land use can release more greenhouse gases into our atmosphere. In addition to methane and nitrous oxide, pesticide and fertilizer use can increase when forests are converted into agricultural lands. In addition, clearing can increase exposure to soils that contain large amounts of stored carbon; when these soils are turned over or disturbed by farming activities, they release additional carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Deforestation, land-use change and other environmental impacts can cause more greenhouse gas emissions than they do. It can also affect regional air quality. As an example, deforestation smoke has been shown to reduce visibility and cause respiratory illnesses such asthma and other conditions. These changes in local air quality can have a cumulative effect on global climate change through higher temperatures resulting from more sun reaching the surface of the planet due to reduced aerosol particles in the atmosphere which usually scatter some sunlight away from the Earth's surface.
In conclusion, deforestation and land-use change have resulted in a significant contribution to increased levels of global greenhouse gas emissions and have had negative impacts on local air quality that further contribute to climate change. Reducing these practices should be a high priority if serious efforts toward mitigating climate change are to take place promptly.
What is the current status of the global climate, and how is it changing in the future?
The global climate is currently experiencing unprecedented uncertainty and change. Unprecedented levels in atmospheric carbon dioxide are causing global temperatures to rise significantly. This can lead to droughts and heat waves as well changing rainfall patterns, melting Polar ice caps, ocean acidification and rising sea levels.
These changes have already had a significant impact on ecosystems across the globe, leading to habitat loss and extinction. They are also threatening the lives and livelihoods of billions of people, particularly those in areas already facing resource scarcity and poverty.
Because of the increase in average surface temperatures from human activity, the number of extreme weather phenomena such as hurricanes and cyclones has been increasing steadily over time. This trend will continue as temperatures continue rising.
A rapidly changing climate has many effects. They can impact everything from food insecurity to displacement by extreme weather events to sea level rise, causing communities to relocate. Climate change is also exacerbating existing social inequalities by disproportionately affecting marginalized communities that do not possess the resources or knowledge necessary for adapting effectively.
While progress has been made in some countries in terms of reducing carbon emission or developing renewable energy programs, there has yet to be any meaningful action taken at a global scale that would allow us to address these issues effectively. In order for us to prevent further disruption and devastation from climate change all nations must come together and take urgent action now while at the same time planning for adaptation in an increasingly uncertain world.
What is the role of greenhouse gases in climate change?
Climate change is influenced by greenhouse gases. They act as an invisible layer around the Earth trapping infrared radiation. This warms the atmosphere. Without them, our planet would be much cooler than it is now.
Greenhouse gases are generated through human activity, such as burning fossil fuels or other industries that produce emissions. As these activities continue to increase, more heat gets trapped in the atmosphere, leading to rising temperatures and extreme weather events.
Carbon dioxide (CO2), the most potent greenhouse gas, is released by fossil fuels like gas, oil, and coal. Climate change is also caused by major greenhouse gases like methane (CH4) and nitrous oxides (N2O).
The concentration of greenhouse gases has increased significantly since preindustrial times due to human activities. This has led to global warming and an increase in temperatures all over the world, as well as in our oceans. It's also causing changes like more severe storms and droughts as well as melting glaciers and rising sea level.
To avoid further damage from climate change, humans need to reduce their emissions of greenhouse gases by transitioning away from fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources like solar or wind power. Reforestation and other agricultural practices can be used to absorb more CO2 from air. These activities will reduce atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations and create a healthier environment that supports all life.
How does climate change affect extreme weather events?
Global warming directly links extreme weather events like heat waves, floods. droughts. cyclones. storms. Global warming has caused an increase of atmospheric temperatures.
Climate scientists claim that the frequency of extreme weather related disasters has more then doubled since 1980. As sea temperatures rise, so do wind patterns. This impacts the normal distribution of storms or hurricanes in different areas across the globe.
2015 El Nino brought warm water towards South America. This led to increasing temperatures at an alarming pace and heavy rains that caused floods and displacement in Peru, Bolivia and other countries. Several places including Antarctica have recorded their highest-ever temperatures indicating a definite relation between global warming trends and the occurrence or frequency of extreme weather events around the world.
Another example is Hurricane Irma which took place in 2017 causing $50 billion of economic loss not just to the USA's Florida but also to other states such as Puerto Rico, Cuba, etc proving once again that climate change is responsible for a dramatic increase in major storms.
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), concluded human activities are increasing climate change's severity. This in turn leads to more frequent and severe natural disasters across the globe. Therefore, strong evidence is available regarding our relationship with extreme weather events happening at frequent intervals all around us.
What is the potential of new technologies to combat climate changes?
This global problem is a huge challenge that new technologies can address. We can now transition to a more sustainable tomorrow by utilizing renewable energy sources such as solar, wind and geothermal, as well energy storage systems like thermal tanks or battery packs.
Carbon capture and sequestration are two methods that can be used to lower greenhouse gas levels. Enhanced agricultural practices can reduce livestock emissions and soil degradation. Smart grid technology can also be used with existing power infrastructure for an efficiency boost, and improved building design can help minimize energy consumption.
In addition, cutting-edge synthetic biology approaches allow scientists to develop organisms that can utilize green sources of fuel such as CO2 laser into usable biofuel or alternate feedstock. This could make transportation more efficient if the market moves away from petrol-powered vehicles and towards zero-emission electric cars that are powered by clean energy.
Finally, investing in digital technology and AI will help people from all over the world gain access to information about their environmental footprint and make informed decisions about how they consume. Understanding our contribution to carbon production is crucial for us all to be better stewards.
How will climate change impact the world's oceans?
What will climate change do to the oceans and marine life of the world?
Climate change has been significantly affecting the world's oceans and the associated marine life since its onset. The constant oceanic heating caused by the loss of the ozone layers causes severe disruptions to marine ecosystems, leading to coral bleaching and species declines.
Climate change can also be linked to unpredictable weather and stronger storms. This can cause extreme sea level rises that can prove fatal for coastal areas. Furthermore, changes in temperature may reduce oxygen levels in water systems resulting in "dead zones" where abundant marine life becomes sparse.
Ocean acidification is also caused by carbon dioxide that is released into the air and then accumulates in the seas. Ocean acidification alters the pH balance, which makes it impossible for some animals, like oysters, crabs, and clams to adapt.
Higher temperatures can also change the location or shrinkage of natural habitats, making them less suitable for some species. Ocean stress increases already high extinction rates worldwide, creating a severe imbalance of predators and prey which might lead eventually to complete extinction.
The effects of climate change ripple throughout entire ecosystems influencing multiple species whether directly or indirectly through evaporation lowering water volumes or sharp temperature shifts jeopardizing any sustainable development for fisheries and other maritime activities. The effects of climate change continue to impact the lives of entire species on this planet.
What is the status of international efforts to tackle climate change?
The current state of international efforts to address climate change is one of unprecedented unity and momentum. Countries all around the globe are increasingly joining forces to find solutions to climate change.
The Paris Agreement, which has galvanized global action and provides a framework for countries to establish voluntary targets to reduce their emissions, serves as a framework. Additionally, the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is providing political guidance and piloting new initiatives such as carbon market mechanisms.
Other regions are seeing progress. The European Green Deal is a comprehensive legislation package that seeks to create a European economy with sustainability as its core. Countries on the African continent also have committed to The African Renewable Energy Initiative, which aims increase Africa's participation in global renewable energy production.
Along with policy changes, action can be observed across all sectors and industries. Cities are actively moving toward sustainable public transport systems. Society as a whole is moving towards more sustainable lifestyles. Companies invent technologies that reduce carbon emissions. Investors are shifting their capital away to renewables.
Through the Common Reporting Framework (CFR), the 2021 Guidelines, the rich countries that are members of the OECD committee have agreed to common standards for reporting their national climate change actions.
All these efforts are a sign of the unprecedented importance given to climate action. If we are to meet the Climate goals as set out by science and enshrined into international law, governments, civil society, and private sector stakeholders must all continue to build on this momentum.
Statistics
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to educate your community about climate change and mobilize action
Climate change education can take many forms - from online resources and interactive educational tools to classroom activities, simulations, and experiential learning programs. The key elements of effective climate change education are:
-
Practical knowledge of the subject is essential for people to be able to make informed decisions.
-
Demonstrating the many ways individuals can make positive changes
-
Involving participants in an open dialog about potential solutions
-
inspiring action through shared experiences
By providing comprehensive climate change lessons for both students and adults alike, educators will be able to help their communities develop strategies for reducing their environmental footprint.
A unique way to engage people in meaningful dialog is to link scientific research with real world examples. Participants also have the opportunity to observe positive outcomes and learn from them, which can lead to further innovation or replication within their organizations.
Participants are empowered by incorporating action-oriented activities in educational curriculums. This gives them the mental tools needed to create campaigns, petitions, and take local actions. It also allows them to be agents for social and political change or sustainability improvement initiatives. Additionally, highlighting individual agency highlights the importance for participants in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and also showcases their collective contributions towards a bigger outcome. Additionally, involving stakeholders early on in policy-making efforts encourages active engagement in decision-making processes allowing them to become involved at all stages of the process which could result in more equitable outcomes for all parties affected by the policy design decisions. With concerted efforts to increase public understanding of climate change and taking appropriate action to limit greenhouse gas emissions, it might be possible to create an environment where these urgent matters can be addressed quickly with attention given where needed most. Together we may be able one day to ensure that successful implementation measures will be put in place that will help us all reach our collective goals.