
The UNFCCC, or the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (also known as UNFCCC), is an international treaty that regulates greenhouse gas emissions and prevents human interference with the climate. It was negotiated during the 1992 Earth Summit, Rio de Janeiro. It has been ratified in 197 countries.
The UNFCCC had three fatal flaws. It was not established by a formal procedure, its secretariat was too small, and it did not facilitate the transfer environmentally-sound technologies. The treaty was however the first to establish an intergovernmental mechanism to regulate climate change and has since been a key component of many international negotiations.
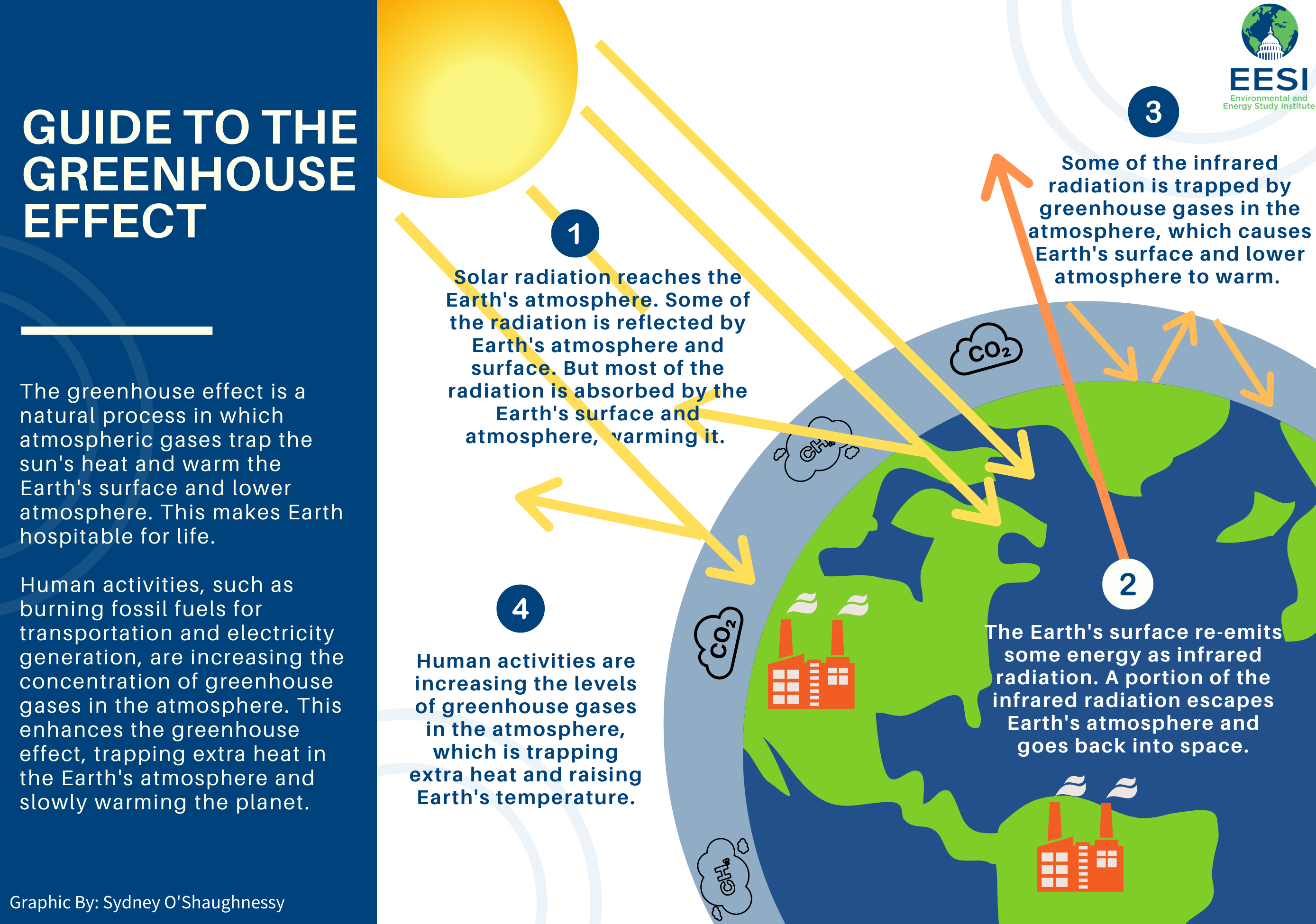
The Convention states that "climate change should not impede sustainable development", and that it should be arrested in a timeframe that allows ecosystems to adapt naturally to climate change. Although it doesn't impose any enforceable requirements on signatories to reduce GHGs, it provides a framework for developing national climate change plans. The UNFCCC acknowledges biological systems' importance in assessing whether climate change must be addressed.
The UNFCCC's principal decision-making agency is the Conference of the Parties. During the COP, governments and representatives from all 190 parties to the convention discuss and debate global climate policy and measures. When a party has ratified the convention, it is obliged to submit its National Communication. A country's National Communication is a report to the UNFCCC on the country's current mitigation and adaptation policies. The National Communication for developing countries must be submitted every four years.
UNFCCC, a key piece in international climate negotiations legislation, has provided the basis for the 2015 Paris Agreement. The agreement is designed to keep the world's average temperature below 1.5 degrees Celsius in the next century, which is lower than the pre-industrial level. Since its creation, the UNFCCC is a source of scientific knowledge that has helped to solve the climate problem.
The UNFCCC also contributes to international policy by focusing attention on the issue of climate change-related extinction risks. This is a topic that has received increasing attention in recent years.

In 2013, UNFCCC established a mechanism called Intended Nationally Determined Contributions. This allows developing countries to customize their plans to fit the needs of their respective countries. The Conference of the Parties can also get timely advice from the Subsidiary Body of Scientific and Technological Advice.
Although the UNFCCC is a crucial step to combat climate change, there are many questions about how effective it has been. Previous COPs set the record for having the largest gathering of global leaders in history. For example, COP23 adopted the Gender Action Plan (GAP), which has guided work on gender-responsive approaches to climate change. Nevertheless the UNFCCC is not facilitating the transfer of environmentally-sound technologies to developing nations. In fact, some Least Developed Countries have not ratified that treaty in the past five years.
FAQ
What is the current state of the global climate and how is it changing?
The current climate is characterized by unprecedented uncertainty and change. Unprecedented levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide are causing temperatures to increase significantly, leading to droughts, heat waves, changing rainfall patterns, melting polar ice caps, ocean acidification, and rising sea levels.
These changes are already having a profound affect on ecosystems worldwide, causing extinctions or disruptions of habitats. They are also threatening millions of people's lives and livelihoods, particularly in areas where there is already resource scarcity.
Due to the higher average surface temperatures due to human activity, extreme weather events like hurricanes, cyclones and wildfires have been steadily increasing over time. As temperatures rise, this trend will likely continue.
The effects of a rapidly changing global climate can be felt everywhere from rising food insecurity to displacement from extreme weather events or sea level rise forcing communities to relocate. Climate change is also increasing social inequality bydisproportionately impacting marginalized communities who lack the necessary resources and knowledge to adapt.
Although there have been some progress in efforts to reduce carbon emissions and renewable energy initiatives in certain countries, it is still not clear that meaningful global action is required to mitigate these changes. For us to avoid further disruption and devastation due to climate change, all nations need to come together and take urgent actions now. At the same time, we must plan for adaptation in an uncertain world.
What are the implications of climate change for the environment and society?
Climate change has many impacts on society and the environment. Rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and decreased air quality are just some of the environmental impacts of climate change. These changes can have severe consequences for human populations. They can lead to instability, increased poverty, insect-borne diseases and altered migration patterns.
Already, climate disruption is already having profound impacts on the environment and society around the world. As global temperatures continue to rise, this is likely to worsen in the near future.
The most significant effect of climate change globally is the rise in ocean levels caused by melting ice caps. This leads to shoreline erosion at many coasts as well as an increased risk for flooding for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion can also happen, affecting freshwater supplies to coastal regions of many countries.
Climate change is causing extreme weather events like heatwaves, droughts and other severe weather to occur in many countries. These events cause massive destruction to homes, businesses, and sometimes even wipe out entire towns. Additionally, severe storms pose additional risks due to flooding or landlides that can increase damage to infrastructure such roads and railways.
Also, wildfires due to climate change are occurring more often than ever. These fires can cause severe damage to habitats and the lives of people living close by.
These dramatic changes in living conditions can often lead to displacement and even refugee crisis when people leave their homes voluntarily or involuntarily due to their changing climate.
The increase in aridity causes dust storms to become more frequent, which makes people suffering from asthma and other respiratory ailments such as asthma even more vulnerable. Additionally, pest infestations are likely to rise significantly in conjunction with higher temperature extremes (a phenomenon known as the "greenhouse bug") which can cause further damage to agricultural production. This could further affect global food security numbers. As fewer crops become available at poorer nutritional qualities, it may bring additional hardships on marginalized communities already struggling to make ends meets otherwise.
How does climate change affect the world's oceans and marine life?
What is the impact of climate change on the world's oceans and marine life?
Since its inception, climate changes have had significant impacts on the oceans of the world and the marine life that surrounds them. The constant oceanic heating caused by the loss of the ozone layers causes severe disruptions to marine ecosystems, leading to coral bleaching and species declines.
Climate change can also be linked to unpredictable weather and stronger storms. This can cause extreme sea level rises that can prove fatal for coastal areas. Changes in temperature can lead to a decrease in oxygen levels, which could cause "dead zone" conditions in which marine life is scarce.
Ocean acidification is also caused by carbon dioxide that is released into the air and then accumulates in the seas. Ocean acidification raises the pH balance which disrupts essential functions of animals unable to adapt such as oysters, clams, and crabs as their shells become weakened.
The effects of higher temperatures on natural habitats can be altered by shifting their geographical locations or shrinking them all together. This could lead to certain species becoming uninhabitable. An increase in ocean stress can accelerate already high extinction rates of many species around the world, resulting in a severe imbalance between predators/prey that could eventually lead to total extinction.
The impacts of climate change have rippled through entire ecosystems. They impact multiple species either directly or indirectly through evaporation, decreasing water volumes, or sharp temperature changes. This could jeopardize any sustainable development for fishing and other maritime activities. Overall climate change continues one by one wiping out entire species from our planet transforming future lives on land but most importantly deep below the surface of our oceans.
Statistics
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Reduce Your Carbon Footprint and Fight Climate Change
There are many actions you can take in order to reduce your carbon emissions and fight climate change. First, invest in energy-efficient appliances and lighting. You can also cut down on energy by not plugging electronics, using public transport, walking, and lowering the temperature in winter and summer.
Second, ensure you recycle all materials and compost food scraps. They won't end up in landfills that release methane gas to the atmosphere. Third, plant trees around your home for shade and natural cooling since vegetation absorbs carbon dioxide from the air. Finally, you can consider buying products with minimal packaging and sustainable labelings like organic cotton or FSC wood. These certifications indicate that it has been sustainably managed over a long period of time to preserve forest health.
Apart from reducing your own emissions, you can also help organizations like Emissions Reduction Alberta and Climate Change Solutions. The Nature Conservancy Canada works towards reducing emissions through clean energie investments and international initiatives such as ICLEI - Local Governments for Sustainability.
Making small changes in our daily lives can help us all fight climate change together.