Earth is known to be the only planet in our solar system that supports life. But how did life start on Earth? Scientists believe that early forms of life existed before the planet was developed. They also believe that there are many more species on the planet than are currently known.
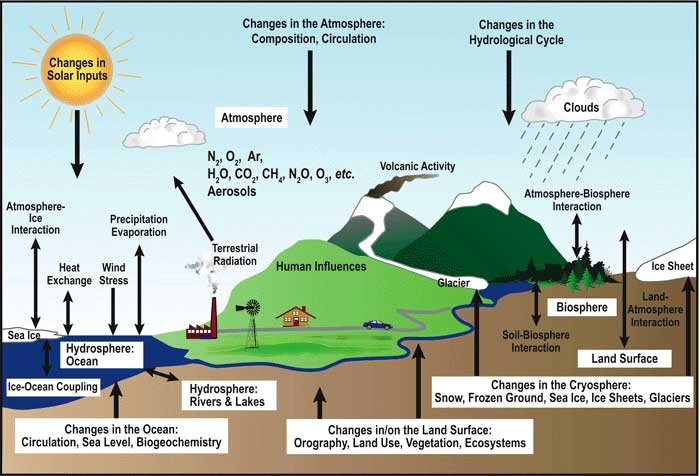
Life on Earth depends on a steady supply of water. This is done through the water cycle. It involves three phases. The oceans hold the most water on the planet. However, there are large rivers and lakes. Additionally, underground aquifers are home to liquid water.

As the Earth warms, chemicals rise to the surface, forming the atmosphere. Radioactive elements can be broken down to release heat. Some of this heat can be stored in the Earth's deepest core. Organisms release other radioactive elements into our atmosphere. Scientists believe the outer core's temperature is between 6,700 and 7,800 degrees F. However the inner core could be much hotter.
During the early days of life, methanogens produced elevated levels of methane in the early atmosphere. The formation of the ozone filter was possible because these methane molecules blocked ultraviolet light waves from reaching the ground. A few years later, organisms started to form on Earth's surface.
The Earth's surface also changed due to these changes. Eventually, rain started to fall. There were also some changes in the seasons. This was due in part to uneven heating of the sun.
The sun would eventually turn into a giant red. The Earth would become more spherical due to its gravitational force. This caused the equator to point toward the sun, and the North and South poles to point away from it.

Another alteration in the planet's fate occurred when a massive impact struck Earth. Some of the basic ingredients for the moon were ejected. Most of the heavier things fell to the middle of the planet. Lighter stuff rose up to the top. The earth was liquid at the time.
Earth is round today and has the shape of a doughnut. Although it measures 12,700km (7,900miles) in diameter, its circumference is larger at the Equator. Depending on how fast you travel, you can reach its center in approximately five to seven km.
The lithosphere, as well as the mantle, make up 84% each of the planet's volume. The mantle is made of molten rocks, while the lithosphere is composed primarily of heavy rock. The Earth's surface lies 80 to 550 kilometers higher than the lithosphere.
The mantle contains rock that has been melted through volcanic eruptions. As the temperature of the Earth increases, the pressure in the mantle increases. The molten rocks are forced to the surface. When a volcano erupts, it releases lava, which creates heat that rises to the surface.
FAQ
What is the relationship between climate change and extreme weather events?
Global warming is directly connected to extreme weather events such a heat wave, floods or droughts, cyclones storms, hurricanes, and cyclones. Global warming has led to increased atmospheric temperatures.
According to climate scientists, the frequency of extreme weather-related catastrophes has more than doubled in the past 20 years. As the ocean temperature rises, so does the frequency of extreme weather-related disasters. This impacts the normal distribution of storms or hurricanes in different areas across the globe.
The 2015 El Nino event caused warm water to move towards South America, leading to rising temperatures at alarming rates and heavy rains that caused floods in Peru (and Bolivia) causing property damage and displacement. Many places, including Antarctica has recorded its highest temperature ever. This is an indication of a strong correlation between global warming trends & the occurrence/frequency of extreme weather phenomena around the globe.
Another example is Hurricane Irma which took place in 2017 causing $50 billion of economic loss not just to the USA's Florida but also to other states such as Puerto Rico, Cuba, etc proving once again that climate change is responsible for a dramatic increase in major storms.
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), concluded human activities are increasing climate change's severity. This in turn leads to more frequent and severe natural disasters across the globe. Therefore, strong evidence is available regarding our relationship with extreme weather events happening at frequent intervals all around us.
What are the environmental and social effects of climate changes?
Climate Change has broad effects on both the environment and society. Rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and decreased air quality are just some of the environmental impacts of climate change. These changes could have serious consequences for humans, causing instability in communities, intensifying poverty, insect-borne illnesses, changing human migration patterns, and destroying essential habitats.
Already, climate changes are having wide-ranging and profound effects on the environment worldwide. As global temperatures rise, this trend is likely to intensify in the near term.
One of the most widespread effects of climate change is the rising ocean levels due to melting of ice caps. This results in coastal erosion and increased flooding risks for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion is also a problem, and can negatively impact freshwater supplies along the coasts of many countries.
Extreme weather events such as heatwaves and droughts regularly occur across many countries around the world as a result of climate change. These events cause mass destruction to homes and businesses, leading to displacement or relocation of communities or wiping out whole towns in some cases. Extreme storms can also cause flooding and landslides, which increase the damage to infrastructure like roads and railways.
The increasing frequency of wildfires that are caused by climate change has also led to devastating consequences for both habitats and those living nearby.
These dramatic changes in living conditions can often lead to displacement and even refugee crisis when people leave their homes voluntarily or involuntarily due to their changing climate.
Dust storms are also increasing in severity worldwide due to increased aridity. This makes it more difficult for asthma sufferers and other respiratory conditions. Pest infestations will increase due to higher temperatures - a phenomenon called the 'greenhouse bug'. This can further impact global food insecurity as fewer crops are available with poorer nutritional qualities, potentially creating additional hardships for marginalized populations that otherwise would be barely able to make ends meet.
What is the effect of land use changes and deforestation on climate?
Deforestation and land use change have a direct and immediate impact on the climate. Trees that are cut down or burnt can no longer absorb carbon dioxide. This is one of the most important greenhouse gasses on Earth. The atmosphere is less carbon dioxide if trees are removed by deforestation, or burned for agriculture purposes.
Changes in land use can release more greenhouse gases into our atmosphere. To illustrate, if forests are replaced with agricultural lands to support livestock production, fertilizer and pesticide use could increase methane emissions. Additionally, clearing soils rich in carbon can increase the exposure; soils that are disturbed by farming activities or turned over can release more carbon dioxide into our atmosphere.
The impacts of deforestation and land-use change extend beyond just increased greenhouse gas emissions; it can also have an impact on regional air quality. Smoke from deforestation-related burning events has been shown to cause decreased visibility and health problems such as asthma, as well as other respiratory conditions. The cumulative effects of these changes in local air quality could have an impact on global climate change. Higher temperatures can be caused by more sunlight reaching the Earth's surface due to lower aerosol particles.
In conclusion, both deforestation (and land-use) change have been a major contributor to rising levels of global greenhouse gases emissions. Additionally, they have had negative effects on local airquality that has contributed further to climate changes. If serious efforts to mitigate climate change are to be made, it is important that these practices are reduced.
What is climate change? How does it happen?
Climate change refers to the long-term shifts in global weather patterns that are caused by an increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat which causes global temperatures to rise. This can cause a wide range of changes in weather conditions and climate. This could include rising seas, melting glaciers. extreme storms or droughts. Widespread coral reef bleaching.
The main cause of climate change is human activity such as burning fossil fuels for electricity and transportation, cutting down forests, and farming livestock. The planet is heated faster when these activities release large amounts carbon dioxide (CO2) than natural processes, such as volcanic eruptions. These activities also produce more CO2 than volcanoes.
Another major contributor to the global greenhouse gas emission is deforestation. It accounts for around 15-20%. When trees are cut down or burned it releases their stored carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Additionally, forests act as a natural carbon sink that removes CO2 from the air; without this absorptive capacity, carbon dioxide levels will continue to rise with devastating consequences for ecosystems around the world.
Not only does CO2 release into the atmosphere but it also releases other harmful gasses, such as methane(CH4) and nitrogen oxide (N2O). Methane has been used extensively in industrial processes and contributes significantly to atmospheric warming while N2O is emitted primarily from agricultural soil management activities like fertilization or tilling which release excess levels of nitrogen into soil leading to N2O production upon microbial contact.
To reduce climate change, humanity must unite efforts across the political, social, and economic systems to reduce emissions dramatically and move away from our dependency on fossil fuels toward renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power or low-carbon hydrocarbon fuels. Smart solutions that encourage zero-waste living and replace polluting fossil fuels could help reduce atmospheric pollution and heat buildup. By taking responsibility for our impact on our environment we can begin mitigating damage through preservation measures like reforestation projects which help maintain biodiversity while absorbing large volumes of damaging CO2 back into nature providing powerful assistance in addressing the climate crisis and restoring balance for future generations
What is the impact of climate change on biodiversity and ecosystems?
Climate change has many effects on biodiversity and ecosystems. Rising temperatures, changes in extreme weather events and sea levels, as well as increased acidity in the ocean are just some of the issues affecting wildlife and ecosystems today.
These shifts in climate conditions can cause shifts in habitat areas, disrupt food chains or affect population numbers or species distributions, with potentially dramatic consequences for biodiversity and the functioning of ecosystems. Changes in the hydrological cycles can also have an impact on water availability for species that live in aquatic environments.
Moreover, changes to climate result in rising temperatures and more frequent extremes such as droughts and floods which puts more stress on already fragile systems such as coral reefs or tropical rainforests. It is estimated that up to 30% of animal species could become extinct due to climate change by 2050, which would spark a cascade of further losses within ecological communities.
Climate change poses a grave threat to biodiversity, but also to human societies that are dependent on functioning ecosystems to provide food, fresh water and timber. You can mitigate the effects of climate change at all levels by reducing global warming trends. Further, future damages can be prevented with good management practices.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Incorporate Sustainable Practices Into Your Daily Life To Fight Climate Change
You can implement sustainable practices in your daily life by reducing your consumption. You can shop secondhand or borrow items from friends and family instead of purchasing new items every day. Additionally, eating vegetarian meals once or twice a week can help reduce the amount of methane released into the atmosphere from livestock production. Finally, whenever possible, turn off the lights when leaving a room to conserve energy.
A second way to combat climate change is to reduce emissions from transport sources such as cars and planes by carpooling or using public transit instead. You can also choose renewable power sources like solar panels to replace traditional fossil fuels and generate electricity at your home. It is crucial to support measures at the policy level that encourage clean air regulations in order to make climate change mitigation work. Engaging with others on issues such as plastic pollution and deforestation can be hugely beneficial, since it makes citizens more aware of the issue and encourages them to act.