
Africa is one the most vulnerable continents in terms of Climate Change. Climate Change financing is essential to ensure climate-resilient green economic development. It provides funding for adaptation and mitigation projects. These can be met by domestic revenue mobilization, as well as international private financing. In addition, there is an increasing interest in regional carbon pricing initiatives. These initiatives have been proposed by the East African Alliance on Carbon Markets (EAAC) and Climate Finance.
Sub-Saharan Africa is particularly vulnerable to climate change, as the region is already suffering from high levels of nutritional deprivation. The region's rainfed agricultural systems are especially vulnerable to climate change. There is also a rising trend of rural-urban migration that contributes to the increasing urbanization trend in the area. Moreover, a large proportion of the region's population relies on ecosystem services. Despite these factors, the SSA is still the continent with the lowest greenhouse gas emissions. This does not address the full effect of Climate Change, which has a negative impact on human existence and natural systems.

Climate change can alter rainfall patterns and storm intensity. This will lead to changes in hydrological systems and freshwater runoff into estuaries. These changes could exacerbate existing anthropogenic stresses. The abiotic and anthropogenic impacts of Climate Change must be considered in adaptation and mitigation. Under a scenario of warming to 4 degrees Celsius, sea level will rise by up to 1 meter in the SSA.
An assessment of the vulnerability of South African estuaries to Climate Change is necessary to help inform the development of appropriate adaptation and mitigation strategies. This study examines the potential impacts of Climate Change on estuaries and identifies the main stressors.
Climate Change stresses include an increase or decrease in sea level, rainfall, sea ice, and shifts in wind and temperature. These changes are likely affect estuarine functions, including nutrient flows, biochemical regimens, salinity and mouth states. Due to the interplay of land and sea processes, estuaries are dynamic and can vary greatly from one area to another. The spatial resolution of vulnerability assessment must take into consideration topography and the distribution of estuarine, coastal and marine biology.
This study used statistical models, a Coordinated Regional Downscaling Experiment and statistical models to assess the future vulnerability of South Africa's estuaries. Results showed that an increase in inter-annual variability would lead to a decrease of freshwater runoff to estuaries. However, extreme precipitation events increased in the summer for the KwaZulu Natal coast.
Numerous studies have been carried out to assess South Africa's vulnerability to climate changes. These studies use statistical models and coastal topography as well as coastal bio-determinants. However, this review requires a more thorough and consolidated overview.
Estuaries provide habitat for many coastal species and are important feeding grounds and nursery grounds for migrants. They also provide highly productive habitats for fish, shrimp and other aquatic animals.
FAQ
What can we do to help the climate change process?
Climate change can be attributed to human activity. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. (IPCC), human activity is responsible for more that 70% of all global warming.
Burning fossil Fuels: The atmosphere is effected by the combustion of fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas. This adds to already existing levels of atmospheric CO2, which act as a "greenhouse gas" by trapping heat from the sun in Earth's atmosphere and increasing temperatures even further. This can result in an increase in ocean levels due to Arctic ice melting. This creates unpredictable weather patterns that can disrupt food production and threaten human health.
Deforestation is the removal of trees that store atmospheric carbon dioxide in their trunks. This happens when they use it during photosynthesis. Reduced forest cover can also increase albedo, which is the amount of reflected sunlight coming back into space. This reduces solar heat absorption at the surface of the earth and promotes global warming. It also reduces the quality of local air, with deforestation being permanently linked to respiratory problems.
Farming: Between 14% and 18% of global anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions are attributed to animal agriculture each year. Due to the high levels of methane bacteria in animal waste, methane gas is released into the atmosphere in large quantities. Changing your diet to less or no animal products can help reduce this contribution. Smog from ground-level ozone can harm our respiratory system and make our lives more hazardous.
Conclusion: Human activity has had a profound impact on the environment for centuries. However, technology has made it possible to leverage green innovation and make eco-friendly efforts to combat climate change. This will ensure that everyone is safe while prospering in nature.
What role can individuals and communities play in combating climate change?
The biggest challenge we face right now is climate change. It affects all of us and requires our collective attention as well as individual actions to make a real difference.
Individuals have an essential role to play in addressing climate changes and reducing their effects. Your everyday behaviors could include reducing waste, conscious eating, changing your lifestyle, such as becoming vegetarian, choosing sustainable clothing and decor, and using public transport more frequently. They can also be involved in political advocacy, and encourage initiatives within their communities that foster sustainability.
They are also crucial in addressing climate issues on a wider scale. They can adopt policies that reduce emissions. These include reformulating energy models that are based on renewable sources, encouraging efficient infrastructure for bicycle or electric transport, reducing deforestation and encouraging composting systems for waste disposal. Collaboration across different communities and countries is essential for this mission's success.
Moreover, civic education on the threats posed by climate change, as well as on ways to contribute positively towards tackling it needs to be implemented from the early stages of education acquisition throughout lifelong learning opportunities. This will enable individuals to become more aware of the issues and better understand how we are connected with other societies that are similarly affected by global warming.
Employers are ultimately responsible for fighting climate change. They can introduce corporate practices that emphasize sustainability and choose green alternatives whenever they are possible. This will have positive sociological and economic outcomes.
Therefore individuals' actions plus community-wide policies together with business transformation will contribute immensely towards creating solutions against global warming and collectively defending humanity against longer terms harmful effects growing out from climate change.
What are some solutions to climate changes? And how effective do they work?
Climate change is an urgent issue, and it requires immediate attention from government, business, and citizens. Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, increased sea levels, and melting polar ice are clear warnings of a disrupted climate system. Many solutions have been offered to this problem, ranging from technological and behavioral solutions to geoengineering.
Technological Solutions. There are many solutions to climate change that have been developed through technological changes. These solutions include renewable energy sources like wind and solar power, which are reliable sources of clean energy without causing any adverse effects on the environment. Electric cars powered by renewable energy could significantly reduce air pollution in cities by replacing petrol vehicles. Other technological solutions include reforestation programs that increase carbon sequestration in soil and trees, as well as coastal protection system to protect vulnerable locations from rising sea levels.
Making behavioral changes: Simple changes to routines can make a huge difference in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and limiting future climate disruption. Locally produced goods can reduce emissions and transport costs. The use of public or active transportation, as well as reducing cost and air polluting simultaneously, is a good option. In the same way, better insulation in your home can help reduce dependence on gas boilers that heat your homes.
Geo-engineering: Geoengineering involves large scale interventions in natural systems. It is risky due potential unforeseen consequences.
The effectiveness and efficiency of these solutions will depend on how many producers invest in green alternatives. However, incentives such as electric Cars play an integral part in incentivizing alternative solutions. Other than increasing consumer awareness about their utility over time, it is possible to mandate alternative solutions via policies measures. This requires regulatory bodies that are willing to engage players further. Although nontechnological approaches can work at one level; solving the global warming problem requires all parties.
What are the main causes of climate changes?
Climate change is a global phenomenon that has been driven by an increase in human-generated greenhouse gases emitted into our atmosphere, primarily due to fossil fuel burning for electricity and transportation. These emissions lead to a greater amount of sun's energy being trapped in Earth’s atmosphere, which results in rising temperatures.
Climate change can also be caused by population growth, land clearing, destruction of ecosystems and energy consumption, over-grazing, and deforestation. This further reduces the number of naturally occurring carbon sinks that absorb CO2 from the atmosphere. Climate change can also come from natural forces, such as changes in solar energy.
These combined human activities result in overloading Earth's capacity to properly balance its energy budget, leading to an average increase of 1 degree Celsius globally since pre-industrial times. Glaciers melt faster than they form and sea levels rise as oceans absorb most of this heat energy. Other negative consequences include water scarcity, droughts and extreme weather events like flooding and hurricanes.
To avoid further damage, it is crucial that we reduce carbon emissions and take steps to curb our emissions. This will give us a fighting chance against climate change's already serious impacts. Along with reducing our dependence upon fossil fuels to generate electricity, it is important to invest in renewable sources like wind turbines or solar cells that do not emit harmful pollutants into nature. Also, reforestation is a sustainable practice that can restore balance to the delicate planetary cycles which are essential for our survival.
What are the current international efforts to combat climate change?
International efforts to combat climate change are moving at a remarkable pace and with unprecedented unity. Countries around the world are increasingly collaborating on ways to reduce emissions, strengthen resilience against impacts, and invest in renewable energy sources.
The Paris Agreement, which has galvanized global action and provides a framework for countries to establish voluntary targets to reduce their emissions, serves as a framework. The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change and (UNFCCC) provides political guidance, as well as piloting initiatives such a carbon market.
In certain regions, there is progress as well. The European Green Deal, for instance, is a comprehensive set of legislation that aims to rebuild Europe's economy while African countries have committed to the African Renewable Energy Initiative. This Initiative aims to increase Africa’s global share of renewable energy production.
In addition to policy developments, action can be seen across sectors and industries; cities are actively transitioning toward sustainable public transport systems while society as a whole is embracing more sustainable lifestyles; companies are innovating technologies that drive down emissions while investors are reallocating their capital away from fossil fuels towards renewables.
The OECD committee represents wealthy countries and has established common standards for reporting national climate action through the Common Reporting Framework, also called the 2021 Guidelines.
These efforts signify a new level of importance for climate action. Governments, civil society & private sector stakeholders alike must continue to build upon the momentum and push towards even greater ambition & progress if there is any hope of meeting Climate goals set by science & enshrined in international law.
What are the impacts of climate change and global warming on agriculture and food security
Global warming and climate change have an immediate impact on agriculture and food safety. Changes in climate can have an impact on rainfall patterns, temperature, soil moisture, extreme weather, and other aspects of agriculture. This can disrupt farming activities, reduce crop yields and lead to losses of agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures can increase the spread of diseases or pests that can impact crops and can also lead to shifts in the areas suitable for agriculture production. This can lead to higher food costs and worsening nutrition.
Rising sea levels present a new threat. They can inundate agricultural land in many coastal locations, leading to increased salinity in wetlands where important crops grow. The changing climate has a similar effect on livestock production. High summer temperatures can decrease the fertility rates of animals like goats, sheep, cattle, and sheep. This can in turn lead to lower milk yields, which can increase food security across communities.
The relationship between climate change and global warming is a complex one; however, efforts are being made to mitigate these results through adaptation strategies implemented by governments worldwide such as strategic investments in climate-smart agriculture (CSA). This involves encouraging sustainable methods, such a crop rotation technique or the conservation of indigenous seed varieties. This helps to mitigate adverse effects from changing weather or other environmental stressors. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
Farmers around the globe must adopt technology that is more sensitive to climate changes to ensure food security in a changing environment. There must be improvements made to existing infrastructure in order to take the appropriate actions when critical crop thresholds fall. This includes installing stable irrigation networks that provide adequate access water at times when it is difficult for farmers to grow crops. Collaboration between different stakeholders is needed to ensure that the quality nutrition guidelines are adhered to in all climates.
What are the environmental and social effects of climate changes?
The environment and society are both affected by climate change. Climate change can have many effects on the environment. These changes can have serious implications for human populations, creating instability in communities, intensifying poverty and insect-borne diseases, altering human migration patterns, and destroying vital habitats.
Already, climate change is having an enormous impact on the environment as well as societies around the globe. As global temperatures rise, this trend is likely to intensify in the near term.
One of the most prevalent effects of climate changes worldwide is the rise of ocean levels as a result of melting ice cap. This leads to shoreline erosion at many coasts as well as an increased risk for flooding for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion is also a problem, and can negatively impact freshwater supplies along the coasts of many countries.
As a result, extreme weather events such heatwaves or droughts are common in many countries. These events cause mass destruction to homes and businesses, leading to displacement or relocation of communities or wiping out whole towns in some cases. Extreme storms can also cause flooding and landslides, which increase the damage to infrastructure like roads and railways.
Climate change is also causing wildfires to become more frequent than ever before. This can have devastating effects on habitats as well as people living near them.
This drastic change in living conditions is often a result of displacement or even refugee situations. When people decide to leave their homes, either involuntarily or voluntarily, it can be because their town has become too dangerous or not habitable due the changed climate conditions.
Dust storms are also increasing in severity worldwide due to increased aridity. This makes it more difficult for asthma sufferers and other respiratory conditions. The possibility of pest infestations increasing is linked to increased temperature extremes, a phenomenon known "greenhouse bug". This further impacts global food insecurity. A smaller number of crops with lower nutritional quality could lead to additional hardships for those already struggling to make ends met.
Statistics
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
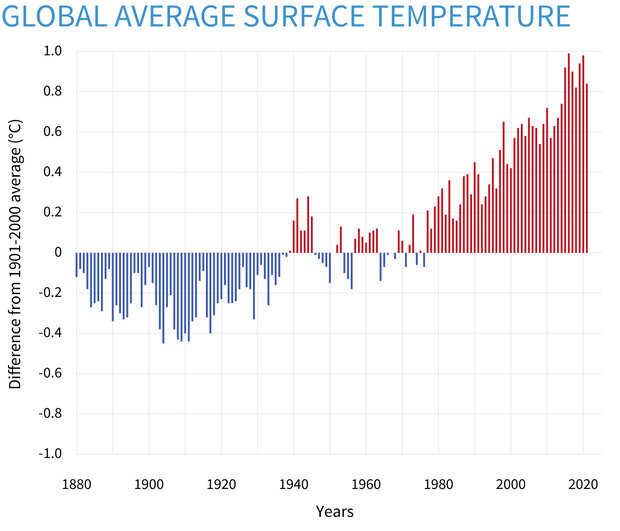
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to Reduce Your Carbon Footprint & Fight Climate Change
There are many ways you can reduce your carbon footprint and combat climate change. First, you can reduce your energy consumption by purchasing energy-efficient appliances, lighting and insulation. You can also save energy by unplugging electronics when not in use, using public transit, walking rather than driving, and turning down the temperature on your thermostat in the winter and summer months.
Second, make sure to recycle materials whenever possible and compost food scraps instead of throwing them away so they don't end up in landfills where they release methane gas into the atmosphere. Third, you can plant trees around the house to provide shade and natural cooling. Vegetation absorbs carbon dioxide in the air. The last thing you should do is to look for products that have minimal packaging and sustainable labels, such organic cotton or FSC certified wood. This means the product has been sustainably managed over time in order to maintain forest health.
Other than reducing your personal emissions, you may also be able to support organizations that work towards lowering global emissions. Organizations such as Emissions Reduction Alberta or Climate Change Solutions; The Pembina Institute; The Nature Conservancy Canada and The Nature Conservancy Canada are all working towards reducing emissions via clean energy investments. International initiatives such ICLEI (Local Governments for Sustainability)'s urban sustainability strategies program can also be supported.
Everyday changes can be made to help fight climate change.