Africa is the most vulnerable continent to Climate Change. Climate Change financing has become a crucial tool for climate resilient economic development. It provides funding for adaptation and mitigation projects. These requirements can be met via domestic revenue mobilization and international private financing. Regional carbon pricing initiatives are also becoming more popular. These initiatives are being considered by the East African Alliance on Carbon Markets, Climate Finance and Climate Finance.
Sub-Saharan Africa has a particularly high level of undernutrition and climate change is a major concern. Its rainfed agriculture systems are particularly susceptible to climatic change. Furthermore, there is a growing rural-urban migration trend that adds to the urbanization trend in the region. A large percentage of the region’s population is dependent on ecosystem services. Despite these factors, the SSA is still the continent with the lowest greenhouse gas emissions. This does not address the full effect of Climate Change, which has a negative impact on human existence and natural systems.

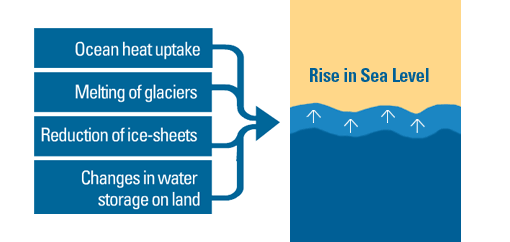
Climate change will have an impact on rainfall patterns and storm intensities, which can lead to changes in hydrological regimes as well as freshwater runoff to estuaries. These changes could exacerbate existing anthropogenic stresses. So adaptation and mitigation should consider the abiotic consequences of Climate Change, as well as existing anthropogenic forces. Under a scenario of warming to 4 degrees Celsius, sea level will rise by up to 1 meter in the SSA.
An assessment of the vulnerability of South African estuaries to Climate Change is necessary to help inform the development of appropriate adaptation and mitigation strategies. This study highlights the most important stressors associated with Climate Change, and how they could impact estuaries.
Key Climate Change stressors include an increase in sea level, a decrease in rainfall and sea ice cover, and a shift in wind and temperature regimes. These changes are likely not to have a positive impact on estuarine systems, such as nutrient and biochemical fluxes, salinity regimes, salt regimes, and mouth condition. Due to the interplay of land and sea processes, estuaries are dynamic and can vary greatly from one area to another. Therefore, a spatial resolution of the vulnerability assessment is needed that takes into account the distribution of coastal and estuarine biology and topography.
This study analyzed the future vulnerability of South Africa's estuaries over the near-future (2035-2035), medium-future (1936-2065) as well as the far-future (2066-2099). The data was obtained using statistical models and the Coordinated Regional Downscaling Experiment. A slight increase in interannual variability could result in a decrease freshwater runoff from estuaries. The summer saw an increase in extreme precipitation, but the KwaZulu–Natal coast was not affected.

Several studies have been conducted to assess the vulnerability of South African estuaries to climate change. These studies use statistical models and coastal topography as well as coastal bio-determinants. This review needs to be more extensive.
In addition to providing essential habitat for coastal species, estuaries are also important feeding and nursery grounds for migrant birds. They are also highly productive habitats that provide food for fish, shrimp, or other aquatic animals.
FAQ
How can the world move towards a more sustainable future in light of the challenges posed by climate change?
Sustainability means being able to provide for current needs and not compromise future generations' ability. In light of the increasing challenges posed by climate change, there is an urgent need for drastic action to eliminate our dependence on finite resources and shift towards a more sustainable approach to how we use them.
We must reexamine how we consume and produce energy, as well as our dependency on natural resources like fossil fuels, if we are to make a transition towards a more sustainable future. We need to find new technologies, renewable energy sources, and systems that can reduce harmful emissions and still meet our daily needs.
Furthermore, it is crucial to take a holistic approach to sustainability. This means that all aspects are considered, including the materials used, waste management strategies and reuse strategies, as well energy usage in transportation and industry. A wide range of potential solutions exists including the utilization of renewable energies such as solar, wind, and hydropower; better waste management systems; increased efficiency in agriculture; improved transport networks; green building regulations; and sustainable urban planning initiatives.
To achieve this goal, we need to make behavioral changes in order for people from all walks of society to be successful. Education programs are needed which will support people in understanding the issues related to climate change and how they can contribute positively towards a more sustainable world through micro-actions such as reducing food waste or adopting low-carbon lifestyles.
Only through cooperation between citizens, business leaders, and governments will we ever be able make substantial progress towards creating a sustainable world for future generations.
What are the causes for climate change
Climate change is a worldwide phenomenon caused by an increase of human-generated greenhouse gasses emitted into the atmosphere. This is mainly due to fossil fuel burning for power and transportation. These greenhouse gases trap more heat from the sun, which causes global warming.
Other factors contributing to climate change include population growth, land clearing and destruction of ecosystems, deforestation, energy consumption, and over-grazing. This also reduces the number naturally occurring carbon sinks, which absorb CO2 from atmosphere. Changes in solar radiation and other natural forces can also contribute to climate changes.
The combined human activities have led to an increase in Earth's energy budget that has resulted in a global average temperature rise of 1 degree Celsius since preindustrial times. Because oceans absorb the majority of heat energy, glaciers are more likely to melt than they ever form. Other consequences include water shortages, droughts, and extreme weather events such as floods and hurricanes that are caused by heavy rainfall on saturated soils.
To protect ourselves from further damage, it is essential for us to reduce our carbon footprint and start curbing our emissions now so that we have a fighting chance against the already significant impacts of climate change. It is vital to reduce our dependency on fossil fuels for electricity production. Additionally, invest in renewable resources such as solar panels or wind turbines. These sources are not harmful to the environment. Also, reforestation is a sustainable practice that can restore balance to the delicate planetary cycles which are essential for our survival.
What is the current global climate? And how is it changing over time?
The current climate situation is one of uncertainty and unprecedented change. Unprecedented levels in atmospheric carbon dioxide are causing global temperatures to rise significantly. This can lead to droughts and heat waves as well changing rainfall patterns, melting Polar ice caps, ocean acidification and rising sea levels.
These changes already have a profound effect on ecosystems all over the globe, causing habitat destruction and extinctions. They also threaten the livelihoods and lives of billions, especially in areas that are already suffering from resource scarcity and poverty.
Due to the higher average surface temperatures due to human activity, extreme weather events like hurricanes, cyclones and wildfires have been steadily increasing over time. This trend is expected to continue into the future as temperatures continue to climb.
A rapidly changing climate has many effects. They can impact everything from food insecurity to displacement by extreme weather events to sea level rise, causing communities to relocate. Climate change is also exacerbating existing social inequalities by disproportionately affecting marginalized communities that do not possess the resources or knowledge necessary for adapting effectively.
Although there have been some progress in efforts to reduce carbon emissions and renewable energy initiatives in certain countries, it is still not clear that meaningful global action is required to mitigate these changes. We must all work together now to stop further disruptions and destruction from climate change.
How are extreme weather events related to climate change?
Global warming directly links extreme weather events like heat waves, floods. droughts. cyclones. storms. Global warming has caused an increase in atmospheric temperatures. This has had an impact on different weather phenomena worldwide.
Climate scientists say that the average frequency of extreme weather-related disasters had more than doubled since 1980. As sea temperatures rise, so do wind patterns. This impacts the normal distribution of storms or hurricanes in different areas across the globe.
Warm water was pushed towards South America by the 2015 El Nino event. This caused rising temperatures to alarming levels. Heavy rains also caused flooding in Peru and Bolivia, causing displacement and property damage. Many places, including Antarctica, have experienced their highest temperatures ever. This indicates a direct relationship between global warming trends as well as the frequency or occurrence of extreme weather events all over the globe.
Another example of climate change at work is Hurricane Irma. It was a major storm that struck Florida in 2017, causing economic losses of $50 billion.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) concluded that human activities are increasing the severity of current climate change which naturally leads to more frequent, severe, and intense natural disasters globally hence bringing forth strong evidence regarding humans' relation to extreme weather events occurring at frequent intervals around us all.
What is the contribution of human activity to climate change?
Human activity is one of the major factors contributing to climate change. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Changes (IPCC), more than 70% global warming has been caused by humans since the middle of the 20th century.
Burning fossil Fuels: The atmosphere is effected by the combustion of fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas. This creates more atmospheric CO2, which acts like a "greenhouse" gas, trapping heat and increasing temperatures. This causes higher ocean levels, as Arctic ice melts. It also scrambles weather patterns across the globe, leading to dangerous storms, droughts, floods and other problems that can affect food production and human health.
Deforestation: Deforestation knocks out trees which sequester atmospheric carbon dioxide in their trunks when they take it up during photosynthesis. Deforestation also raises albedo (the amount of reflected solar radiation that is returned into space) and reduces solar heat absorption by earth's surface, thereby promoting global warming. As well decreases local air quality with deforestation being linked permanently with respiratory issues.
Farming: The animal agriculture industry contributes 14%-18% of total anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases globally every year. Because animal waste is rich in methane bacteria, large amounts of methane are released into the atmosphere. This can lead to a significant increase in global warming.
In conclusion, while human activity has had an adverse impact on our environment for centuries, technological advances have made it possible to turn our attention towards the future. We can leverage technology through green innovation to help us move forward in our efforts to reduce climate change and keep everyone safe.
Statistics
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Invest In Clean Energy and Support the Transition To A Low-Carbon Future
Clean energy is renewable energy that doesn't emit greenhouse gases or produce polluting emissions. It includes technologies such as solar photovoltaic, wind power, hydroelectricity, geothermal energy, and hydrogen fuel cells. Clean energy investments can provide many environmental benefits. They reduce dependence on fossil fuels and help to reduce air pollution.
By buying shares in companies involved in developing clean energy technologies, investors can get involved in these projects. This includes investing in publicly traded stocks, mutual funds and ETFs (exchange traded funds) that are related to renewable energy. To fund research and development in clean energy technologies, investors can also make direct investments in venture capital or start-ups.
Investors in clean energy support innovation that reduces the harmful effects of traditional sources of electricity generation. This investment can also help increase economic development through the creation of jobs in the production and engineering of renewable energy systems. Lastly, investors may see a return on their investment in clean energy through tax incentives programs. These incentives encourage green technology investments such as solar panels, wind farms, and biomass heat production systems.
We can both support the transition from low-carbon to a low carbon future by investing in companies that are focused on producing electricity from renewable resources like sun, wind, water and avoid activities that may harm the environment.