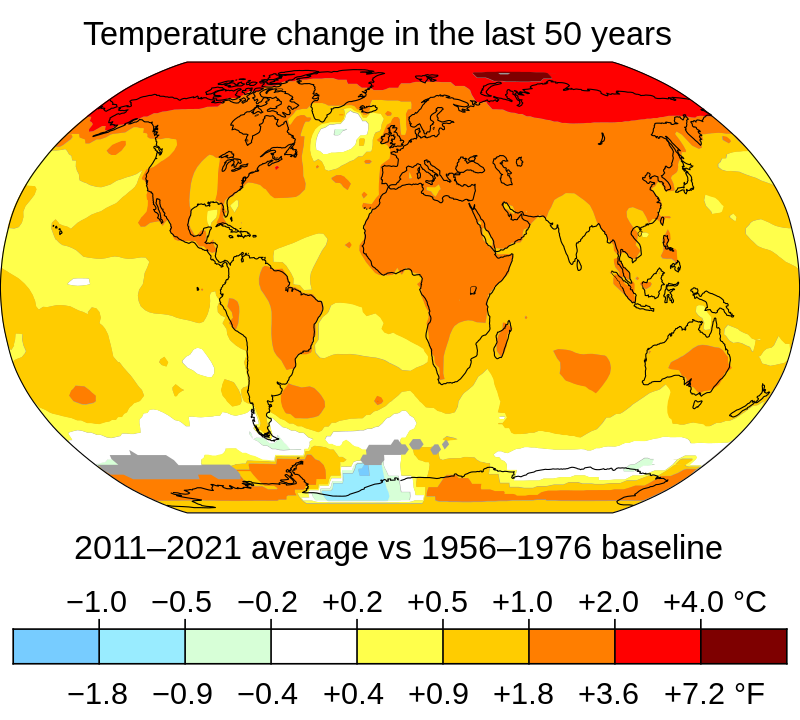
Global temperature data shows variations in the oceans and atmosphere. These temperature changes and their consequences can have adverse effects on many natural processes including agriculture. They can also lead to sickness and death. An increasing number of extreme heatwaves has caused millions to lose their lives and threatened the ecosystems around the world. Certain regions are more affected by climate change than others.
Since 1981, the global average temperature has increased by nearly 2 degrees Fahrenheit. It has also risen at an average rate of 0.18 degrees Celsius per decade. This is well above the long-term trend in warming. It is actually twice the long-term trend.
The current rate of warming is greater than the previous two warmest decades, which were the 1980s and 1990s. This change in temperatures has had a major impact on a wide range of areas, from areas that are drier to higher-latitude regions. It has also increased the intensity and potential impact of tropical cyclones.
As of January 2020, the global average temperature surface is almost 0.8 degrees Celsius higher than the preindustrial average. Many regions are already at 1.5 degrees Celsius. That level has not been seen for a decade. During the past three decades, global warming has exceeded 0.2 degrees Celsius per decade, a rapid rate that will likely increase in the coming years.
According to a report from the World Meteorological Organization, 40% of global average temperatures will reach 1.5 degrees Celsius in the next five-years. Some of these years (e.g. 2021) are projected to be amongst history's warmest.
Although there have been some exceptions, most of the Earth's surface experienced warmer temperatures than average in the first nine month of 2015. The average temperature in most countries was above average. However, some regions experienced record high temperatures. Other regions, like the southern United States of America and parts South America were among the most hot in recorded history.

Since the late 1970s, the United States has warmed at a faster rate than the global average. This trend has slowed in recent years. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, the average global temperature has risen at an average rate of 0.17 degrees Celsius per decade. This is slightly less than the average increase in 48 contiguous states.
Climate change denier claim that global temperatures are not a concern because they have remained stable for decades. Global surface temperature has increased much faster than it has declined, and scientists have found a direct correlation in climate change and extreme weather events.
According to the Goddard Institute for Space Studies in 2010, the average global ocean and land temperature was 1.2° Celsius higher than the 1850-1900 mean in 2010. This average is expected rise to 1.1-1.15° Celsius by 2022, according to the institute. If the rate of increase continues, that will put us on track to exceed 4 degC by the end of the century, which would result in unprecedented heat waves and severe drought in many regions.
FAQ
How does human activity affect climate change
Climate change is due in large part to human activity. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change(IPCC) states that humans are responsible more than 70% for global warming in the past 20 years.
Burning Fossil Fuels: Burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This creates more atmospheric CO2, which acts like a "greenhouse" gas, trapping heat and increasing temperatures. This can result in an increase in ocean levels due to Arctic ice melting. This creates unpredictable weather patterns that can disrupt food production and threaten human health.
Deforestation: Trees that sequester atmospheric CO2 in their trunks during photosynthesis are destroyed by deforestation. Also, cutting down forests can increase albedo - which is the amount reflected solar radiation going back into space. It also reduces solar heat absorbtion by the earth's surfaces and encourages excessive global warming. Deforestation is also associated with respiratory problems and local air quality.
Farming: The animal agriculture industry contributes 14%-18% of total anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases globally every year. Due to the high levels of methane bacteria in animal waste, methane gas is released into the atmosphere in large quantities. Changing your diet to less or no animal products can help reduce this contribution. Smog from ground-level ozone can harm our respiratory system and make our lives more hazardous.
In conclusion, human activity has been drastically impacting our environment for centuries now, but with rapid advances made in technology such as renewable energy sources availability we have started turning our heads towards the future leaving behind carbon-emitting heavy industries results will soon start speaking themselves clearly when we leverage on technology through green innovation paving away toward eco-friendly efforts combatting climate change efficiently keeping everyone safe under prosperous nature purview.
What are some of the proposed solutions to climate change and how effective are they?
Climate change is a pressing issue that requires urgent attention from citizens, governments, businesses, as well as citizens. Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, increased sea levels, and melting polar ice are clear warnings of a disrupted climate system. Numerous solutions have been suggested to deal with this phenomenon. They include technological solutions as well as behavioral changes and geoengineering.
Technological Solutions: There are many technological solutions that can be used to combat climate change. These include renewable energy sources like solar power and wind power that provide reliable sources for clean energy while causing minimal harm to the environment. Electric cars powered with renewable energy could dramatically reduce pollution in cities and replace petrol vehicles. Other technological solutions include reforestation projects that aim to increase carbon sequestration in trees and soil as well as coastal protection systems to protect vulnerable places against rising ocean levels.
Behavioral changes: Small adjustments to existing routines can make big differences in reducing emissions. This will help limit future climate disruption. For example, purchasing locally produced goods with shorter supply chains reduces emissions associated with transport costs for food. Using public or active transportation instead of personal cars also optimizes the use of resources and brings down cost and air pollution simultaneously; similarly opting for more efficient home insulation can reduce reliance on gas boilers for heating homes reducing emissions also lowering bills over time.
Geo-engineering (GEO): This involves large-scale interventions into natural systems that may be too risky because of potentially unforeseeable consequences.
The effectiveness and efficiency of these solutions will depend on how many producers invest in green alternatives. However, incentives such as electric Cars play an integral part in incentivizing alternative solutions. Other than increasing consumer awareness about their utility over time, it is possible to mandate alternative solutions via policies measures. This requires regulatory bodies that are willing to engage players further. Although nontechnological approaches can work at one level; solving the global warming problem requires all parties.
What is climate and how does it affect us?
Climate change is the long term shift in global weather patterns resulting from an increase of greenhouse gases. These gases trap heat, leading to global temperature rises that can result in a range of climate and weather changes. These can include rising sea level, melting glaciers or droughts, widespread coral bleaching, species extinction and disruptions in food production.
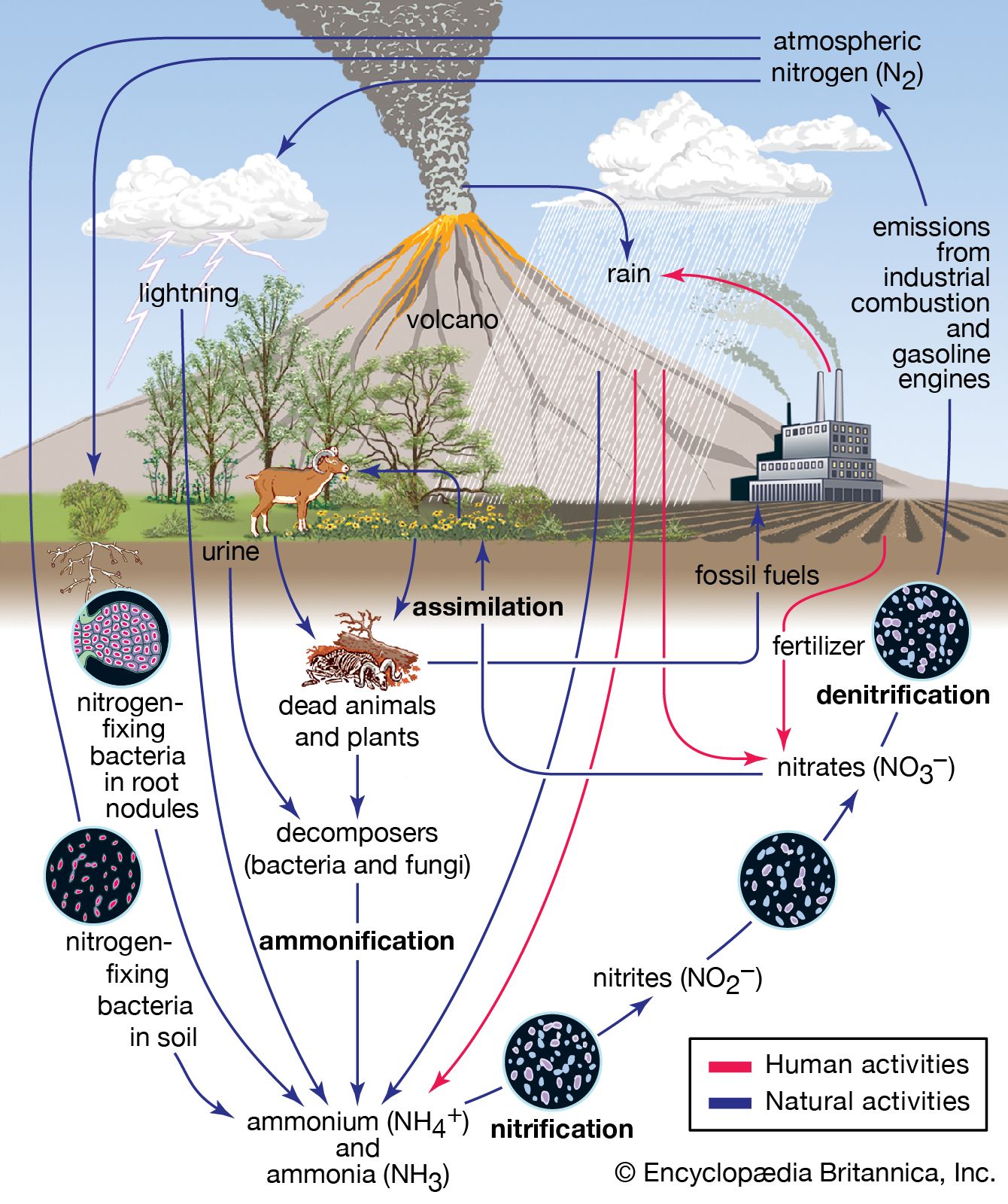
Human activity is the major cause of climate change. When these activities release massive amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere it warms the planet at a much faster rate than natural processes like volcanic eruptions as these activities produce many times more emissions than volcanoes.
Another major contributor to the global greenhouse gas emission is deforestation. It accounts for around 15-20%. Trees are destroyed or burned to release their carbon dioxide. Forests are also a natural carbon-sink that removes carbon dioxide from the air. Without this absorption capacity, carbon levels will continue increasing with devastating consequences for the ecosystems around the globe.
Other than CO2, human-caused pollutants also release other dangerous gases such as methane and nitrous oxide (N2O) into the atmosphere. Methane has been extensively employed in industrial processes. It contributes significantly to the atmosphere's warming. While N2O can be emitted primarily by agricultural soil management activities, such as tilling or fertilization which release excess nitrogen to soil.
To minimize climate change humanity must make concerted efforts across social, economic, and political institutions to reduce these emissions drastically and transition away from our dependence on fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources such as solar, wind power, or low-carbon hydrogen fuels. Replacing technologies that use polluting fossil fuels with smart solutions that promote zero-waste living could be an effective approach to decreasing atmospheric contamination while simultaneously reducing heating due to CO2 accumulation. We can take responsibility for how we impact the environment and begin to mitigate it. Preservation measures such as reforestation help preserve biodiversity while also absorbing large amounts of harmful CO2 back into the natural world. This is a powerful way to address climate change and restore balance for future generations.
What are the implications of climate change for the environment and society?
Climate change has many impacts on society and the environment. Climate change can have many effects on the environment. These changes can have severe consequences for human populations. They can lead to instability, increased poverty, insect-borne diseases and altered migration patterns.
Already, climate changes are having wide-ranging and profound effects on the environment worldwide. As global temperatures rise, it is likely that this trend will continue in the near future.
Global climate change has one of the most powerful effects on ocean levels. This causes shoreline erosion along many coastlines and increases the risk of flooding for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion also occurs, negatively affecting freshwater supplies in coastal regions in many countries around the world.
As a result, extreme weather events such heatwaves or droughts are common in many countries. These events lead to massive destruction of homes, businesses, and even the loss of whole communities. Intense storms increase the risk of flooding and landslides. This can further damage infrastructure like roads, railways, and bridges.
The increasing frequency of wildfires that are caused by climate change has also led to devastating consequences for both habitats and those living nearby.
Such drastic changes in living conditions often result in displacement or even refugee crises when people move away from their homes either voluntarily or involuntarily because their towns have become too dangerous or no longer habitable given their altered climate conditions against which they cannot cope adequately.
Increased aridity also increases dust storms worldwide with unhealthy air pollution caused by these making it difficult for people who suffer from respiratory illnesses such as asthma especially vulnerable. Furthermore, pest infestations are predicted to rise in tandem with warmer temperatures. This phenomenon is known as the 'greenhousebug'. Global food insecurity will continue to grow as fewer crops have lower nutritional qualities. This could potentially lead to more hardships for people already struggling to make ends work.
How are developing countries and communities affected by climate change?
Due to limited access, technology, and healthcare systems, developing countries, communities, are particularly vulnerable to the consequences of climate change. Changes in temperature, precipitation, and sea levels increase pressure on already scarce resources, with floods and droughts wearing away at already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can cause a drop in crop yields which will adversely impact the poorer communities that are struggling to feed their families. Extreme weather events like hurricanes or heatwaves can also cause destruction to infrastructure, causing further economic inequality.
The long-term implications of climate change include continued resource scarcity, poverty, and health impacts including an increased number of vector-borne diseases such as malaria or dengue fever. A rise in sea levels and extreme weather events will lead to increased flooding. This could put lives at risk in coastal regions, where there is often a lack of emergency services or infrastructure. These risks can be mitigated by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. However, other measures may be required such as better management of freshwater resources or easier access to healthcare facilities that aid in the prevention of diseases like malaria.
Statistics
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Educate Your Communities About Climate Change and Mobilize Action
Climate change education can take many forms - from online resources and interactive educational tools to classroom activities, simulations, and experiential learning programs. These are the essential elements of effective climate education:
-
People are equipped with practical knowledge
-
Demonstrating that people can make a real difference.
-
Engaging participants in an open discussion about possible solutions
-
Inspiring action through shared experiences
Teachers can help communities to reduce their environmental footprints by offering comprehensive lessons in climate change for both adults and students.
Connecting scientific research and real-world examples creates a unique opportunity to engage audiences in a meaningful discussion. Exploring case studies and best practices also provides participants with opportunities to witness positive outcomes firsthand, which can inspire further innovation or replicable measures within their own communities or organizations.
Participants are empowered by incorporating action-oriented activities in educational curriculums. This gives them the mental tools needed to create campaigns, petitions, and take local actions. It also allows them to be agents for social and political change or sustainability improvement initiatives. A focus on individual agency emphasizes the importance and benefits of participation in reducing carbon emissions. However, it also highlights participants' collective contribution to a larger end result. A key element in policy-making is to involve stakeholders as early as possible. This encourages their active involvement at every stage of the process and could result in better outcomes for all. If we work together to improve public understanding and to take the appropriate action to reduce greenhouse gases emissions, then we might be in a position to create an environment that allows us to address urgent issues with our attention being focused where it is most necessary. In this way, we can all help to achieve our collective goals.