
The phrase "climate under crisis" has become synonymous to the dangers posed by global warming. It has been used to call for aggressive climate change mitigation. The climate crisis does not only concern climate change. It is about how people react to the climate crisis and make decisions. It can also have a tremendous psychological effect.
Climate in Crisis examines how climate change and global warming affect people, communities and the planet. This book examines the impacts of climate change on Indigenous communities and the ways they are impacted.
Many environmental activists are protesting climate change's impact on extreme weather events as it leads to more of them. Some of these activists and scientists are scientists. Other people are farmers, who are adopting more sustainable practices.

The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change states that the climate of Earth is changing rapidly. We may also experience an increase in extreme heat, severe precipitation, drought, and other climate-related phenomena if we do nothing. Even the planet's ocean levels are increasing. These changes can not be reversed.
The most vulnerable are pastoralists who live in rural areas and nomadic communities. The Northern Triangle of Central America (El Salvador-Guatemala, Guatemala, Honduras and Mexico) has seen droughts and floods increase in recent years. These conditions have impacted rural economies and led to flooding. 75,000 Kenyans could face flooding by the riverine if they don't take adequate measures to reduce emissions.
Many experts predict that climate change will lead to an increase of suicide, substance abuse, mental illness, and other problems. The ACA Climate Change Task Force reported that people living in disadvantaged areas are more likely to be affected by climate change trauma.
Climate in Crisis also discusses the effects of environmental colonialism upon Indigenous people. In Panama, for example, Indigenous communities had to cope with deforestation, logging, as well as the migration of people from their ancestral homelands.
Costa Rica has seen its urban growth accompanied by a concern for sustainability. Several environmental advocates believe that the media has not done a good job of highlighting this issue. There are many ways that media can communicate the climate issue better.
In order to understand why the climate crisis is so significant to people, researchers at the Political Psychology Research Group studied a number of Americans. Most Americans believe that Earth is warming. It is also a serious problem according to 85% of respondents. However, almost half the respondents doubted that the warming was caused by human activity.
Despite this, most of the respondents still believed that climate change is real. The public's view on climate has not changed, even though the political debate has moved. However, technology is still lacking to address the climate crisis.
The story can sometimes be distorted by soundbites and inability to analyze. The majority of issues, however are split approximately 50-50.
FAQ
How are developing countries and communities affected by climate change?
Due to their lack of access to resources, health care systems, and technology, communities and countries in developing countries are more vulnerable to climate change. Temperature, precipitation, sea levels, and rainfall changes put additional pressure on already scarce resources. Additionally, floods and droughts cause havoc in already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can reduce crop yields. This will impact communities with low incomes and food insecurity. Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and heatwaves, can cause the destruction of infrastructures and displacement of people, which further perpetuates economic inequality.
Climate change will have long-term effects on resources, poverty, and health. This includes an increase in the number of vector-borne disease such as dengue fever or malaria. A rising sea level and extreme weather events will increase the risk of flooding, putting lives at stake in coastal areas that often lack the infrastructure or emergency services required to evacuate. While mitigating greenhouse gases is essential to build resilience to these risks, there are other options available. These include better management of freshwater resources and easier access for health facilities. This helps with the prevention of diseases such as malaria.
What role does climate change play in greenhouse gas emissions?
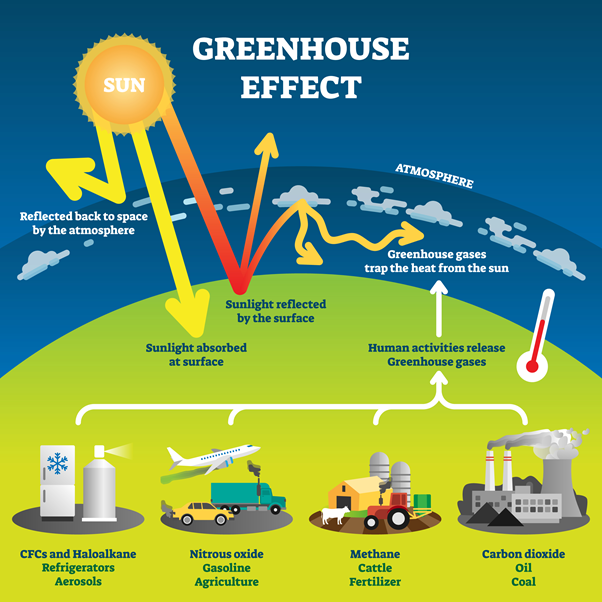
Greenhouse gases are a key factor in climate change. They act like an invisible blanket around the Earth, trapping infrared radiation and warming the atmosphere. Without them, our planet would be much cooler than it is now.
Greenhouse gases are generated through human activity, such as burning fossil fuels or other industries that produce emissions. These activities are increasing in number, which means that more heat is trapped in our atmosphere. This can lead to extreme weather events and rising temperatures.
The most prevalent greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide, which is released from fossil fuels, such as oil, gas, and coal. Other major contributors to climate changes include methane, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases (F-gases).
Because of human activities, the concentrations of greenhouse gases have increased substantially since preindustrial days. This has led both to global warming and an increase worldwide in temperatures, as well as increased ocean levels. It is also causing changes such as more intense storms and droughts, melting glaciers, and rising sea levels.
To avoid further damage from climate change, humans need to reduce their emissions of greenhouse gases by transitioning away from fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources like solar or wind power. You can also reduce greenhouse gas emissions by reforestation and adopting farming methods that allow soil to absorb more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. These activities will lower the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gasses and make the Earth a more healthy place for all life.
What is the potential impact of land-use change and deforestation upon climate change?
Climate change is directly affected by land use changes and deforestation. If trees are cut down, or burned, carbon dioxide, one the most important greenhouse gases, is no longer absorbed. Carbon dioxide is therefore less removed from the atmosphere when trees are deforested or burned for agricultural purposes.
Land use changes can also increase the atmospheric concentration of greenhouse gases. When forests are cleared for livestock production, the use of fertilizer and pesticides may lead to an increase in methane or nitrous oxide emissions. Also, clearing can increase soils containing large amounts of carbon; these soils may be exposed to farming activities that turn them over or disturb them, which will release more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
The effects of land-use change, deforestation, and increased greenhouse gas emissions can have a negative impact on the quality of regional air. Deforestation can lead to reduced visibility, health issues such as asthma and other respiratory problems. These changes in air quality can have a cumulative affect on global climate change. The increase in temperatures is due to more sun hitting the Earth's surfaces.
The deforestation of land and the resulting changes in land-use have made a significant contribution towards increasing global greenhouse gas emission levels. These impacts have also had a negative impact on local air quality which has further contributed to climate change. If serious efforts towards mitigating climate changes are to be made quickly, then reducing these practices must be a priority.
How can we address climate change by addressing the role of the energy industry?
The role of the energy sector in climate change is immense. The primary cause of global warming is the burning of fossil fuels. It releases carbon dioxide into our atmosphere and traps heat. This causes an increase of average temperatures.
This requires energy sources to move away from carbon emitting sources like natural gas and coal, and instead shift towards renewable energy sources, such solar, wind, or geothermal. This shift can be made possible by both government policy and incentives as well investments in innovative technology like hydrogen-fuel cells. Businesses and homeowners can cut their emissions while reducing their electricity bills by investing in infrastructure that supports these renewable sources.
Other methods include transitioning away from polluting transportation options like petroleum-fueled cars and moving towards electric vehicles or public transport. The government has great power to help societies transition away from oil-based infrastructures. They can support research into battery technology and encourage consumers to invest in cleaner modes.
To reduce carbon footprints, companies should adopt green business practices. For example, better insulation in offices and production facilities. This can drastically reduce operational expenses while also improving environmental performance metrics.
These initiatives must not only be supported at the company level, but also at the federal level to be truly successful. Taxing pollution products increases individuals' willingness to adopt healthier practices. But this won't force them to compete with polluters. Instead, vouchers or subsidies for low carbon products will create a continuous market to support sustainability. The private and public sector must work together to combat climate change. Providing vouchers or subsidies for low-carbon products and switching to cleaner energy sources will create a market that supports sustainability efforts.
What are some of the proposed solutions to climate change and how effective are they?
Climate change has become one of the most urgent issues of our time. It requires government, businesses and citizens to pay attention. Climate disruption is obvious by rising temperatures, melting polar ice, extreme weather, higher sea levels and increasing sea levels. Multiple solutions have been proposed to address this phenomenon. These solutions range from technological solutions to behavioral changes to geoengineering.
Technological Solutions: An array of solutions have arisen to address climate change through changes in technology. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind power provide reliable, clean energy that has minimal environmental side effects. By replacing petrol cars, electric cars that are powered by renewable energy can significantly reduce the amount of air pollution in cities. Another technological solution is reforestation projects, which aim to increase carbon sequestration and soil.
Behavioral Changes: By making simple alterations to established routines can make a big difference in reducing emissions and limiting future climate disruption. Locally produced goods can reduce emissions and transport costs. By using active or public transportation to transport your goods, you optimize your use of resources and bring down costs and air pollution. Also, insulation can be more cost-effective and help reduce the dependence on gas boilers in heating your home.
Geo-engineering (GEO): This involves large-scale interventions into natural systems that may be too risky because of potentially unforeseeable consequences.
The effectiveness and efficiency of these solutions will depend on how many producers invest in green alternatives. However, incentives such as electric Cars play an integral part in incentivizing alternative solutions. Other than increasing consumer awareness about their utility over time, it is possible to mandate alternative solutions via policies measures. This requires regulatory bodies that are willing to engage players further. Although nontechnological approaches can work at one level; solving the global warming problem requires all parties.
Statistics
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to Educate Your Communities About Climate Change and Mobilize Action
There are many ways to learn about climate change education, including online resources and interactive tools, classroom activities, simulations and experiential learning programs. These are the essential elements of effective climate education:
-
arming people with practical knowledge about the subject
-
demonstrating ways that individuals can make a difference
-
Involving participants in an open dialog about potential solutions
-
Inspiring action through shared experiences
Teachers will be able help their communities reduce their environmental footprint by providing comprehensive lessons on climate change for students and adults.
Connecting scientific research and real-world examples creates a unique opportunity to engage audiences in a meaningful discussion. Participating in case studies and learning from best practices provides the opportunity to see positive results firsthand. This can encourage further innovation or replicateable actions within their own organizations.
Participants will be able to use their mental skills, such as petition-writing, campaign creation, or local action, to help them become social and political agents or sustainably improvement advocates. Moreover, emphasizing individual agency highlights the importance of participation in reducing emissions while also demonstrating participants' collective contributions towards a larger outcome. Participating early in policy-making helps to encourage active participation. This allows for more equitable outcomes. Through concerted efforts at increasing public understanding of the impacts of climate change coupled with taking appropriate action on mitigating greenhouse gas emissions, we might be able to create an environment where these pressing matters are addressed urgently with attention applied where necessary most so that together we may one day be able to ensure successful implementation measures that will help us reach our collective goals out ahead time as well.