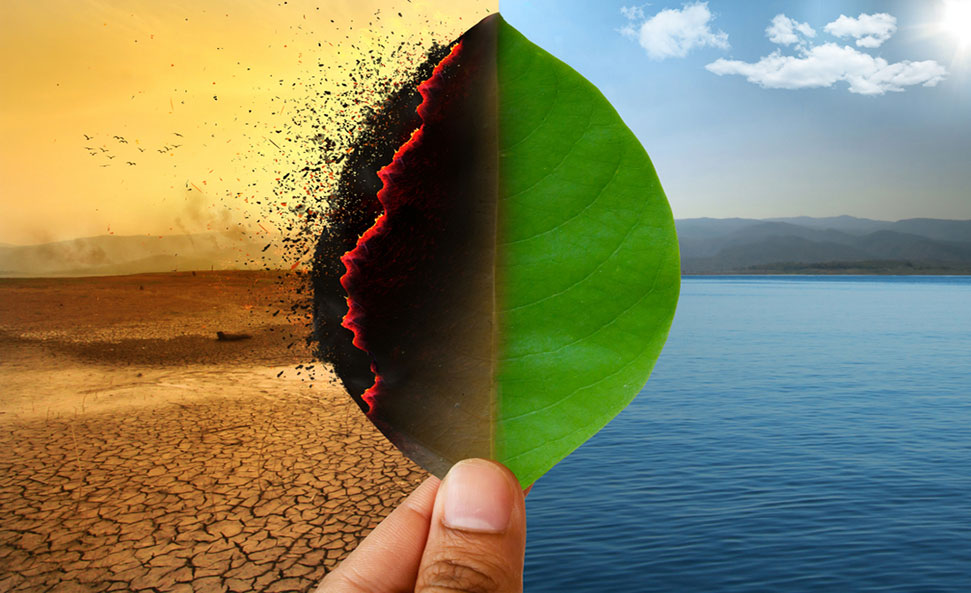

Climate change can be described as "an increase in the average long-term weather conditions due to human activities". These changes can occur due to many causes, including the emission of greenhouse gases. Climate change can have a significant impact on the economy as well as on human health. It is a global concern that will affect every day life. The science behind climate can be used to help citizens address it.
Global warming is a topic that many scientists are currently studying. Climate modeling is a method of predicting how temperature will change over time. Some studies forecast changes in precipitation and snow. Scientists are also finding evidence that ocean acidification as well as sea level rising are real.
Extreme weather events are becoming more common as part of global warming. They can also be much more intense. As a result, more carbon is being released into the atmosphere from industrialization and fossil fuel burning.
Additional factors that contribute to climate changes include short-term temperatures variability, long term temperature variability, ocean acidification, and greenhouse gases. The main reason for climate change is human activity.
Scientists are becoming increasingly convinced that climate change is caused primarily by fossil fuel burning. Recent years have seen nearly all of the world's annual greenhouse gas (GHG-) emissions be attributed to industrialized countries. Although many countries have set emission reduction targets, they aren't meeting most of their goals. Thus, there are ongoing negotiations to create more specific emission-reduction targets for industrialized states.
When it comes to climate change, interpreters must understand the full range of perspectives, cultural influences, and scientific explanations. The interpreter should be able to understand the political, economic, and social aspects of climate science. You should also be up-to-date on all the latest information.

The United States Geological Survey defines global warming as an increase in global temperatures. Climate models predict that changes in the ice and snow may also occur. Other changes can also be caused by climate change to ecosystems and biodiversity. The economic impact of climate change is also a concern.
In 1992, UNFCCC was established. The Rio Earth Summit brought together industrialized nations to commit to reducing GHG emissions by 2000. This target is unlikely to be met. That is why the world's seven largest economies called on the UN to establish an expert group to study the issue.
The IPCC is an international organization dedicated to climate change research. This body creates reports on the science of climate change. The group has published dozens upon reports since its 1990 release. Each report is supported by scientists from around the world.
Although it's not possible to completely avoid the negative impacts of climate changes, adaptation attempts to minimize these effects. Technology, the mitigation and conservation of resources, are some of the ways that adaptation can be achieved.
FAQ
How does the politics of climate change impact global efforts to address it?
Climate change is a controversial issue that has caused a lot of division between nations, governments and individuals. The implementation of measures to address climate change is affected by the political stances of various actors. It has become difficult to find consensus on global efforts to tackle this pressing environmental crisis.
A majority of scientists agree that climate change caused by humans is real and must be addressed immediately. Politics surrounding these issues can often hinder global cooperation, which is required to make effective progress in implementing sustainability energy practices and upholding regulations protecting natural environments, researching viable technological options, and other climate-change interventions.
In particular, various governments around the world are keen to protect their economic interests and enforce measures that would limit business activities as little as possible; this frequently conflicts with the regulations that experts recommend for addressing climate change in an efficient manner. It is very difficult for any one state or group of countries to effectively address climate change without strong commitments from all participants and broad-scale international action.
Differences in power dynamics among countries further complicate gaining full consensus on how best to tackle climate change. Countries with greater economic power are more likely to elect their own representatives to the international bodies responsible for negotiations on the environment. This can cause lopsided discussions about the interests of each country versus the collective interest all parties. Additionally, the potential side effects of implementing radical changes like geoengineering are being heavily debated at both national as well international levels.
Also at the grassroots level, grassroots movements have fought against powerful opponents such as corporate ownerships. These lobbies are trying to preserve politically favorable positions for their industry especially when it is about funding research into alternative sources of energy production or enforcing Renewable Energy Technology mandates. If individual governments want to make valid progress in the subject matter themselves instead of seeking short-term benefits or spectacles, they must be clearheaded about possible outcomes.
It is essential to distribute resources properly to any intervention program, and to be mindful of political divisions within nations, if we want to see an effective coordinated effort to mitigate our current environmental crisis.
What impact does climate change have on biodiversity and ecosystems
Climate change can have a variety of impacts on biodiversity, ecosystems, and the environment. Climate change is affecting ecosystems and wildlife today.
Changes to climate conditions can have drastic consequences for biodiversity and the functioning ecosystems. Water availability can be affected by changes in hydrological cycles.
Climate changes can lead to higher temperatures and more frequent extremes (such as droughts) which put more stress on already fragile systems, like coral reefs or tropical forests. Up to 30% of all animal species could be extinct by 2050 due to climate change, which would lead to further losses in ecological communities.
Climate change poses a grave threat to biodiversity, but also to human societies that are dependent on functioning ecosystems to provide food, fresh water and timber. It is essential to mitigate its effects at all levels. Future damages must be avoided by careful management.
What are the environmental and social effects of climate changes?
Climate change has many impacts on society and the environment. Climate change is causing a variety of environmental problems, including rising temperatures, extreme weather, sea level rise, and reduced air quality. These changes can have severe consequences for human populations. They can lead to instability, increased poverty, insect-borne diseases and altered migration patterns.
Already, climate disruption is already having profound impacts on the environment and society around the world. Global temperatures are expected to continue to rise and this will only get worse in the future.
One of the most prevalent effects of climate changes worldwide is the rise of ocean levels as a result of melting ice cap. This can lead to shoreline erosion and increased flood risk for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion can also happen, affecting freshwater supplies to coastal regions of many countries.
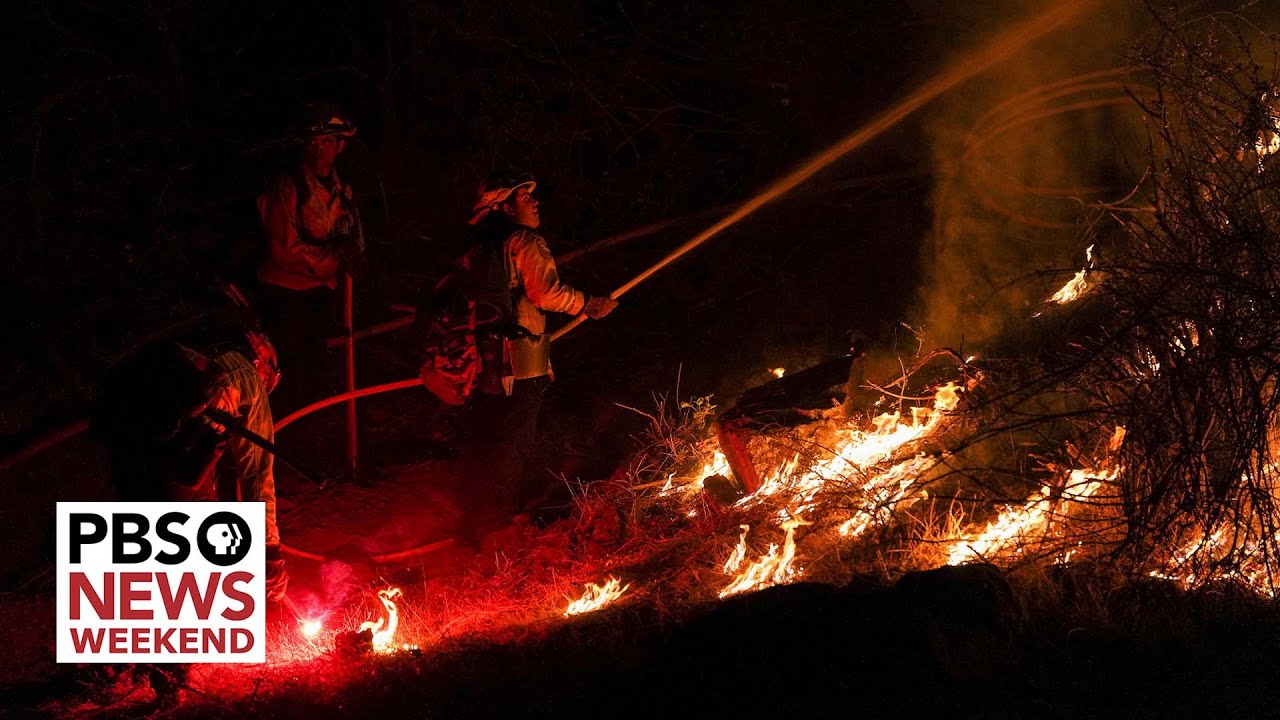
Due to climate change, extreme weather phenomena such as heatwaves/droughts frequently occur across many countries in the world. These events cause massive destruction to homes, businesses, and sometimes even wipe out entire towns. In addition, intense storms create further risks related to flooding or landslides that increase damages to infrastructure such as roads and railways.
Additionally, wildfires caused climate change are more common than ever. They can be devastating for both the habitats and the people who live nearby.
Many people are forced to flee their homes due to drastic changes in their living conditions.
An increase in aridity means that dust storms can occur more frequently, making people with asthma and other respiratory illnesses like asthma particularly vulnerable. Pest infestations will increase due to higher temperatures - a phenomenon called the 'greenhouse bug'. This can further impact global food insecurity as fewer crops are available with poorer nutritional qualities, potentially creating additional hardships for marginalized populations that otherwise would be barely able to make ends meet.
Statistics
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Educate Your Community About Climate Change and Mobilize Action
Climate change education can take many forms - from online resources and interactive educational tools to classroom activities, simulations, and experiential learning programs. The key elements of effective climate change education are:
-
People with practical knowledge on the subject
-
demonstrating ways that individuals can make a difference
-
Engaging participants in an open discussion about possible solutions
-
Shared experiences inspire action
Teachers can assist their communities in reducing their environmental footprint by teaching them comprehensive lessons about climate change.
It is also possible to connect scientific research with real-world examples, which can be a unique way of engaging audiences in meaningful dialogue. The best practices and case studies can provide participants with the chance to experience positive outcomes firsthand. This can help them innovate or create replicable measures in their own communities.
Participating in action-oriented activities within educational curriculums gives participants the mental tools they need to create campaigns, form petitions or take local actions. This empowers them to become agents for social and/or political transformation or sustainability improvement. Additionally, highlighting individual agency highlights the importance for participants in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and also showcases their collective contributions towards a bigger outcome. Stakeholders should be included early in policy-making, which encourages participation at all stages. This will result in equitable outcomes for all parties. With concerted efforts to increase public understanding of climate change and taking appropriate action to limit greenhouse gas emissions, it might be possible to create an environment where these urgent matters can be addressed quickly with attention given where needed most. Together we may be able one day to ensure that successful implementation measures will be put in place that will help us all reach our collective goals.